[ad_1]
I hear from loads of groups that they wrestle to estimate properly: “We’re actually unhealthy at estimating,” they are saying. They know the causes to estimate product backlog objects, so that they wish to get higher.
Too usually, although, these groups will try to enhance by attempting tougher. They don’t determine issues of their method and systematically repair them, they only attempt tougher.
I’m a mediocre chess participant. I’m not going to win extra video games by simply attempting tougher. To win extra video games, I have to determine the place I’m weak and work to enhance in these areas.
A group that simply “tries tougher” to estimate properly received’t change a lot. And finally the futility of getting higher by solely attempting tougher turns into demotivating. At that time some groups throw within the towel and take an angle that estimating is unattainable so that they received’t attempt.
Estimating is just not unattainable however it’s difficult. As an alternative of giving up, attempt these 7 issues that may assist your group estimate higher.
Earlier than We Start
Every of the following tips is so important to correct estimates that, typically, I’ve written a complete weblog or e book on the idea (or a associated idea) behind nearly each tip. I’ve included hyperlinks to these in your ease of use.
Another factor earlier than we get began: If you realize me, you in all probability know I’m an enormous fan of estimating in story factors. Story factors are an summary relative measure of effort. I’ve undoubtedly obtained story factors in thoughts for the following tips. However they are often utilized simply as properly should you estimate in additional conventional models comparable to particular person days.
Tip 1. Agree on One in all 5 Sorts of Estimates
The primary tip for extra correct estimates is to verify everybody agrees on the kind of estimate being supplied. In case you are giving a extremely conservative, protected estimate however I’m giving a best-case estimate, we’re nearly sure to disagree.
This tip is prime. In case your group doesn’t discuss what kind of estimate you’re making, the one method group members will agree on estimates is by luck.
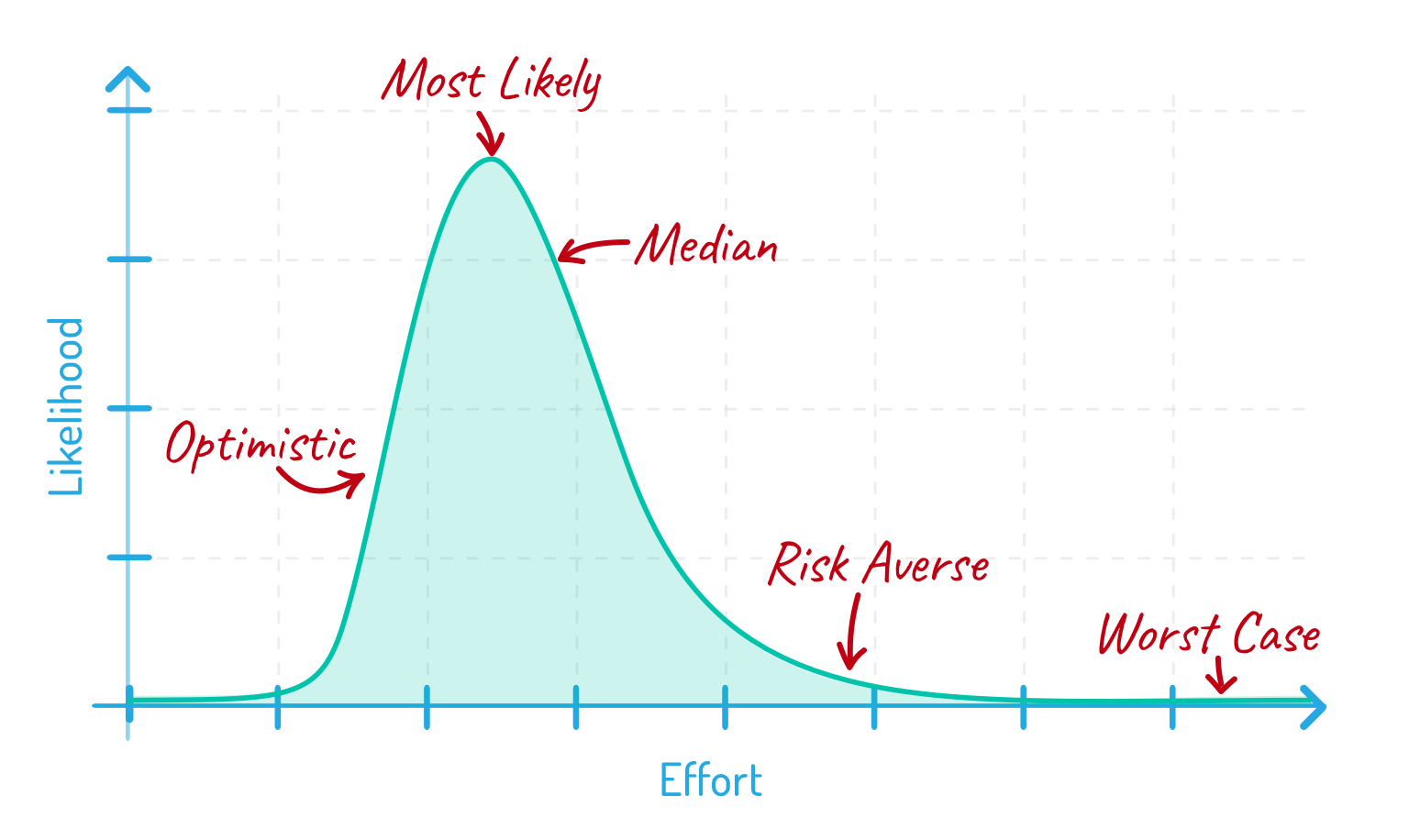
A group can present certainly one of 5 attainable estimates, as proven within the chart under. The chart reveals the probability of being executed at numerous instances. The final form of the curve signifies that there aren’t loads of issues you are able to do to complete one thing a lot earlier, however the lengthy tail signifies there are loads of issues that might go unsuitable to essentially make one thing take longer.
- Single Most Doubtless Estimate: That is the very best level within the chart under
- Perfect Case Estimate: This represents one thing like a ten% probability of accuracy. Just about all the pieces has to go completely for a group to complete on this period of time.
- Median Estimate (50/50 Estimate): The group is simply as more likely to end early as they’re to complete late.
- Danger-Averse Estimate: That is the reverse of the perfect estimate. However the group has a 90% probability of beating the risk-averse estimate.
- Worst-Case State of affairs Estimate: That is situated on the far proper of the chart. Crew members in all probability received’t estimate this conservatively as a result of that represents all the pieces going unsuitable whereas engaged on an merchandise.
 I Advocate Median Estimates
I Advocate Median Estimates
The place on this chart ought to group members estimate? I believe the median is finest. I believe it’s simple for estimators to conceptualize—it’s the purpose the place one thing is equally more likely to take roughly effort.
However crucial factor is to have that dialog with group members so that they’re in settlement about which number of estimate the group needs to make use of. Gaining this settlement removes loads of frustration group members really feel after they have what seem to be futile disagreements over an estimate.
Study extra in regards to the forms of estimates in “The 5 Attainable Estimates and Which One Your Crew Ought to Use.“
Tip 2. Create Relative Estimates by Analogy
The second tip is to estimate comparatively by analogy. For those who’re ever in an estimating assembly with me, you’ll by no means hear me ask, “How lengthy will this take?” As an alternative I ask questions like, “What different backlog merchandise is that this like” or “Will this take roughly time than this different merchandise?”
In my Licensed ScrumMaster coaching class, we do an train the place we estimate dwelling enchancment duties. We begin by agreeing on one thing small, however not the smallest, and maybe calling {that a} 2.
For instance we’d determine that putting in a brand new oven is a 2. All different objects on the record will be estimated relative to this. One thing that may take 4 instances as lengthy would get an 8, and so forth.
Not solely is relative estimating extra correct, groups can do it extra shortly, particularly as soon as a group has constructed up a big base of things to match in opposition to.
With relative estimating, the group doesn’t want to think about all the sub-steps and estimate every after which add them up. They solely want to seek out one thing comparable and use the identical estimate.
There may be additionally some proof that relative estimation by analogy is extra correct (“A Causal Mannequin for Software program Value Estimating Error” & “Software program Effort Estimation: An Exploratory Examine of Professional Efficiency”
For extra on the subject of relative estimation, learn the net e book Estimating with Story Factors.
Tip 3. Maintain Estimates Inside One Order of Magnitude
Third, maintain most estimates inside one order of magnitude comparable to 1–10. Analysis has proven that we’re truly not that unhealthy at estimating objects so long as we keep inside one order of magnitude. That’s why within the agile estimating methodology of Planning Poker, the vast majority of the playing cards are small numbers. We will estimate fairly properly in that vary.
If you might want to estimate outdoors an order of magnitude—and there will be good causes for doing so—construct as much as that steadily. Estimate a dozen or extra objects all within the 1–10 vary then begin reaching somewhat bigger.
Don’t estimate some objects from 1–10 after which go proper to estimating one thing at 100. As an alternative estimate a couple of objects which are somewhat too massive—maybe as much as 20. Then perhaps transfer as much as 40.
Be mindful, although, in lots of circumstances you’d be higher off splitting work this massive into a number of, smaller objects and estimating these as a substitute.
For extra on estimating withing one order of magnitude, learn The Greatest Approach to Set up a Baseline when Enjoying Planning Poker.
Tip 4. Keep away from Getting Too Exact with Estimates
A fourth tip is to keep away from getting too exact. It’s simply too arduous.
It’s apparent you don’t wish to estimate one thing as 3.47 story factors, particular person days, or no matter unit you’re utilizing. Much less apparent, although, could also be that you simply in all probability don’t wish to use 3, 4, and 5 as legitimate estimates. It’s unlikely group members can distinguish between numbers this shut to at least one one other.
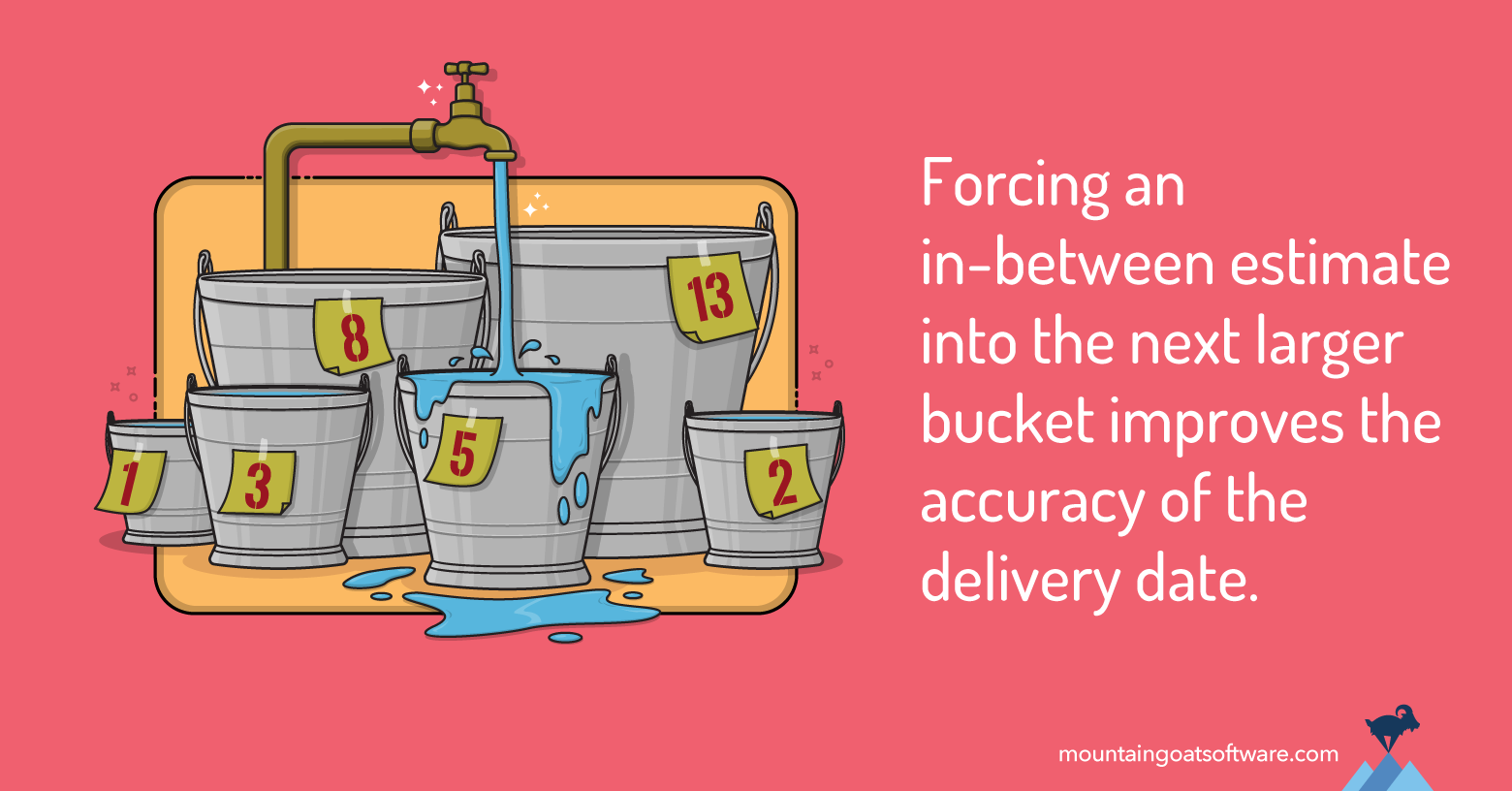
I pre-identify a set of values groups will estimate with. A group may select to estimate utilizing the powers of two 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16. One other group may use the Fibonacci sequence of 1, 2, 3, 5, 8 and 13, which is my slight choice.
The numbers in these sequences will be considered as buckets. For instance, if we’re utilizing the Fibonacci sequence we’d have a 5-point bucket and an 8-point bucket.
The group doesn’t have to exactly estimate how lengthy a given product backlog merchandise will take. As an alternative, the group has solely to place the product backlog merchandise into the best bucket: “Does this merchandise belong within the 5-point bucket or the 8-point bucket?” (Or maybe another bucket.)
This protects time in product backlog refinement by eradicating the stress to be excellent. By eradicating stress, it additionally helps get group members to have interaction within the course of.
Pizza is one other instance we will doubtless all relate to. My native pizza restaurant provides pizzas in 3 sizes: medium, giant, and grand. That’s sufficient. I can inform the distinction between these sizes. In the event that they provided me pizzas in 15 totally different sizes between medium and grand, I wouldn’t be capable of inform the distinction.
And simply as when ordering a pizza, spherical up when group members are debating between two sizes. For those who’re attempting to determine between a medium and a big pizza, order the massive. If the group is torn between 4 and eight, go together with the 8.
Odds are there will probably be some unanticipated work concerned that may push the merchandise towards the upper quantity when the group will get into engaged on it.
I cowl the ideas of story level ranges and rounding up estimates in additional element in “Story Factors Are Greatest Considered As Ranges.”
TIp 5. Triangulate Your Estimates
Tip quantity 5 is to triangulate your estimates. The time period comes from previous crusing ships. A ship’s navigator might work out the ship’s location by taking a look at two objects at totally different factors on the horizon and drawing a line from every on a map. The intersection can be the ship’s location.
We triangulate estimates by evaluating the merchandise being estimated to not less than two different estimates, ideally one which’s bigger and one smaller. For instance, if we’re considering of estimating one thing as 5, you wish to discover maybe a 2 and an 8 to match in opposition to. Ask the group if the proposed 5 appears about twice as massive as the two and somewhat smaller than the 8.
If that’s the case, you’ve obtained affirmation that 5 is an efficient worth for that merchandise. Typically, although, group members will wish to change the proposed worth based mostly on the triangulation. If that’s the case, nice! Triangulating has helped enhance that estimate.
Examine triangulating estimates, and how one can entry our Agile Mentors Planning Poker device.
Tip 6. Keep away from Anchoring
Tip six is to keep away from anchoring. Anchoring refers to offering data to estimators which will unduly affect the estimates they’re about to make.
To know anchoring, think about you’re in a retailer and see a shirt that was beforehand $40 now on sale for $20. The point out of $40 anchors you into considering the shirt is price that a lot. Logically, who cares what worth a shirt used to promote for? Your buy choice must be based mostly solely on the present worth. However that previous worth will get in our head and influences us.
One of many benefits of estimation approaches like Planning Poker is that every particular person supplies a primary estimate free from anchoring by others.
However anchoring can happen in refined methods. A product proprietor could begin an estimating assembly by saying one thing innocent-sounding like, “This assembly ought to go quick right this moment. I solely have 5 objects that want estimates they usually’re all fairly small.”
Saying the objects are “fairly small” will get in estimators’ heads and it’s been proven that phrases like that may unduly affect estimates. So, to get one of the best estimates attainable, coach folks not say issues like that in estimating conferences.
Anchoring is among the causes I keep away from velocity-driven dash planning. Examine why I favor capacity-driven dash planning.
Tip 7. Keep away from the Center Floor
Tip quantity 7 is to keep away from settling disputes by selecting the center worth. A human bias generally known as the central tendency of judgment reveals that we are inclined to favor estimates perceived as being in the course of a scale.
If, for instance, a group estimates with a Fibonacci sequence (1, 2, 3, 5, 8, and 13) it’s doubtless that the center values (3 and 5) will probably be overused as values.
The identical impact will be current when group members are debating which worth to make use of. Somebody will usually counsel settling within the center as a compromise. Whereas the center worth could completely be one of the best estimate, don’t settle there with no thought.
Encourage the estimators with the excessive and low values to make a case for his or her values earlier than going to the center.
Getting Higher at Agile Estimating
Estimating properly is difficult. However don’t throw up your arms. There are steps you’ll be able to take to turn into higher at it.
I’ve shared 7 ideas for a way I assist groups enhance. What different issues have you ever executed to enhance your group’s estimates? Please share your ideas within the feedback as a result of I’d like to learn them.
And should you’re excited about understanding, or serving to your group perceive story factors, take a look at our estimating with story factors video course.
[ad_2]