[ad_1]

Picture created by the writer utilizing Midjourney.
Because the variety of malicious packages revealed on bundle repositories like PyPI and npm continues to extend due to automation, safety researchers are experimenting with alternative ways to make use of generative AI for figuring out malware.
Endor Labs researcher Henrik Plate beforehand designed an experiment to make use of giant language fashions to evaluate whether or not a code snippet is dangerous or benign. In his newest experiment, Plate in contrast OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo with Google’s Vertex AI text-bison mannequin utilizing improved analysis strategies. He additionally compares the efficiency of OpenAI’s GPT-4 in sure circumstances.
In his preliminary experiment, Plate requested the LLMs to categorise open supply software program code as malicious or benign, however on this newest analysis, he requested the LLMs to reply with a threat rating on a scale between 0-9 that ranged from threat scores of little to extremely suspicious. One other enchancment of this analysis was the removing of feedback in suspicious code snippets, which the staff says reduces publicity to immediate injection, or the strategy of manipulating AI responses by means of rigorously crafted malicious inputs.
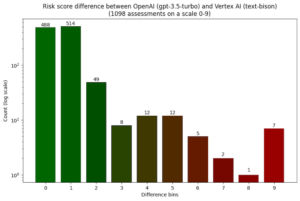
The 2 LLMs agreed in a majority of 1,098 assessments of the identical code snippet, Plate discovered. In 488 of the assessments, each fashions got here up with the very same threat rating, and in one other 514 circumstances, the danger rating differed by just one level.
Plate concluded his preliminary experiment with the concept that LLM-assisted malware evaluations with GPT-3.5 should not but a viable various to guide evaluations. He says an inherent drawback is a reliance on identifiers and feedback written by benign builders to grasp code conduct. These feedback act as an info useful resource however might be misused by malicious actors to trick the language mannequin.
Regardless of being unsuitable for figuring out malware on their very own, Plate says they can be utilized as one further sign and enter for guide evaluations. “Particularly, they are often helpful to robotically overview bigger numbers of malware alerts produced by noisy detectors (which in any other case threat being ignored totally in case of restricted overview capabilities),” he wrote.
On this newest experiment, Plate concludes that the danger evaluation of OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo and the Vertex AI text-bison mannequin are comparable however neither performs tremendously, he says. Each fashions gave false positives and false negatives, and OpenAI’s GPT-4 outperforms each in the case of offering supply code explanations and threat scores for non-obfuscated code.
 Plate and his staff additionally clarify why they consider the danger of immediate injection is extra manageable for this use case in comparison with others, writing, “That is primarily as a consequence of the truth that attackers don’t reside in a world freed from guidelines … they nonetheless must adjust to the syntactic guidelines of the respective interpreters or compilers, which opens up the chance for defenders to sanitize the immediate enter.”
Plate and his staff additionally clarify why they consider the danger of immediate injection is extra manageable for this use case in comparison with others, writing, “That is primarily as a consequence of the truth that attackers don’t reside in a world freed from guidelines … they nonetheless must adjust to the syntactic guidelines of the respective interpreters or compilers, which opens up the chance for defenders to sanitize the immediate enter.”
For the total technical particulars of this experiment, learn Plate’s weblog at this hyperlink.
Associated Gadgets:
Knowledge Administration Implications for Generative AI
Ought to Workers Personal the Generative AI Instruments that Improve or Exchange Them?
AI Researchers Situation Warning: Deal with AI Dangers as International Precedence
coding, Endor Labs, generative AI, GPT-3.5, GPT-3.5-turbo, GPT-4, malicious code, malware, threat evaluation, safety, text-bison, Vertex AI
[ad_2]