
[ad_1]
Researchers flip digital noise disruptions into potential spintronic developments utilizing minuscule vanadium changes in tungsten diselenide, a leap in the direction of environment friendly magnetic switching.
Digital noise, often called Random Telegraph Noise (RTN), has disrupted digital techniques, resulting in sign processing errors. The Heart for Built-in Nanostructure Physics researchers, a part of the Institute for Fundamental Science in South Korea, have unveiled a discovery which may utilise these semiconductor fluctuations. This venture resulted from joint analysis efforts with Joo Min-Kyu from Sookmyung Ladies’s College and KIM Philip at Harvard College.
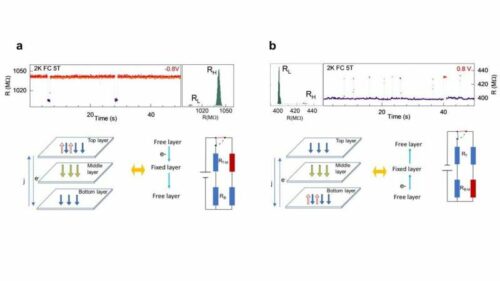
The researchers have discovered that by introducing a tiny quantity of vanadium into tungsten diselenide (V-WSe2), a vdW-layered semiconductor, they will produce important RTN indicators and magnetic fluctuations. Excessive contact resistance in lateral units sometimes hinders the show of pure quantum states, decreasing machine effectivity. The staff developed a vertical magnetic tunnelling junction machine to handle this, inserting a number of layers of magnetic V-WSe2 materials between the highest and backside graphene electrodes. Remarkably, this configuration showcased pure quantum states and generated sturdy RTN indicators with a mere ~0.2% focus of vanadium doping.
The researchers emphasised that the cornerstone of their work was the era of great magnetic resistance fluctuations utilizing vertical magnetic tunnelling junction units with minimal contact resistance. They detected RTNs that displayed a exceptional amplitude of as much as 80% between two clearly outlined steady states. On this bistable state, temperature-driven magnetic resistance fluctuations emerge as a result of steadiness between intralayer and interlayer interactions of magnetic domains. The staff pinpointed this distinctive bistable magnetic state by observing discrete Gaussian peaks within the RTN histogram, showcasing distinct noise energy spectrum traits.
The researchers discovered that by altering the voltage polarity, they might toggle between the bistable magnetic states and regulate the RTN’s cut-off frequency. This opens avenues for utilising 1/f^2 noise spectroscopy in magnetic semiconductors and introduces magnetic switching in spintronics. They imagine this marks an effort to discern the bistable magnetic state by way of substantial resistance fluctuations in magnetic semiconductors, presenting a magnetic switching technique utilizing 1/f^2 noises by way of simple voltage polarity changes in spintronics.
[ad_2]