
[ad_1]
The Cisco Talos report exposes new malware utilized by the group to focus on Web spine infrastructure and healthcare organizations within the U.Okay. and the U.S.

Two studies from cybersecurity firm Cisco Talos present intelligence a couple of new assault marketing campaign from the North Korean risk actor Lazarus. The studies expose new malware and instruments utilized by the group, which retains utilizing the identical infrastructure.
Bounce to:
What is that this new malware assault chain?
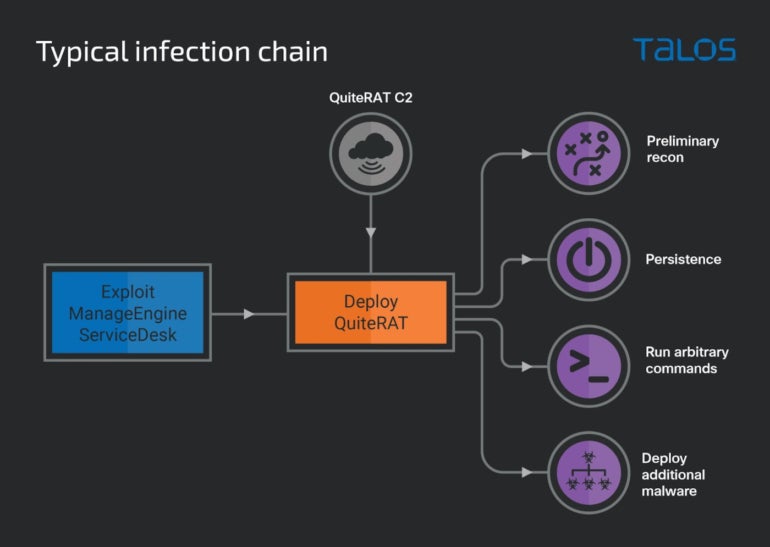
The researchers noticed the Lazarus group efficiently compromise an web spine infrastructure supplier within the U.Okay. in early 2023, deploying a brand new malware dubbed QuiteRAT.
The preliminary compromise was finished through exploitation of the CVE-2022-47966 vulnerability, which impacts Zoho’s ManageEngine ServiceDesk. The risk actor leveraged an exploit for it 5 days after the proof of idea was publicly disclosed. The profitable exploit downloaded and executed the QuiteRAT malware, hosted on an IP tackle utilized by Lazarus since at the very least Might 2022.
As soon as the malware has been executed, it begins sending preliminary details about the system to its command-and-control server and waits for a solution, which may be a direct command to the malware or a Microsoft Home windows command line to be executed through the cmd.exe course of. The preliminary data is being encrypted and despatched to the C2; it consists of community configuration data (i.e., IP tackle and MAC tackle) and the presently logged in person title (Determine A).
Determine A
The Lazarus group’s new arsenal of malware
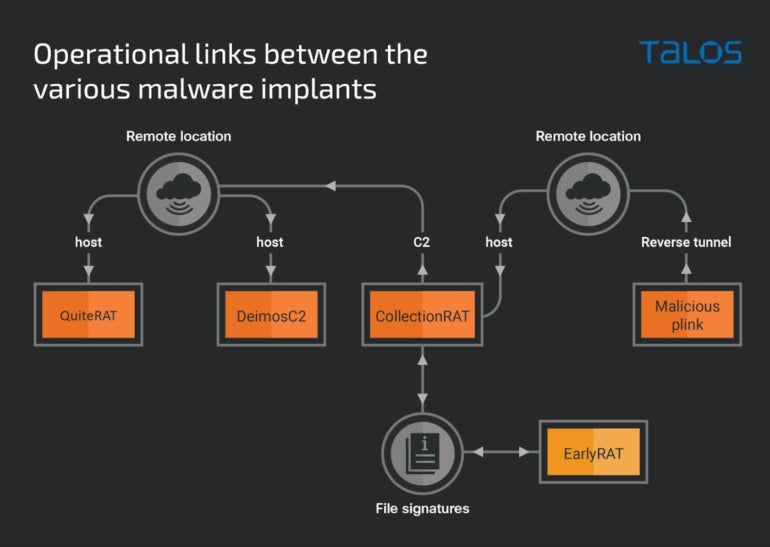
Lazarus has used numerous malware on this assault marketing campaign: QuiteRAT, CollectionRAT, DeimosC2 and malicious Plink.
QuiteRAT
QuiteRAT is a distant entry software principally constructed utilizing Qt libraries and developer code. The usage of Qt for writing malware is uncommon as a result of this framework is often used to develop graphical person interfaces. Qt use makes the code extra complicated to research for reverse engineers, and may render machine studying and heuristic detections by safety options much less dependable as a result of they won’t flag using the Qt libraries as malicious.
It’s not the primary time Lazarus has used the Qt framework for creating malware. MagicRAT malware was already utilizing it, and similarities between each (e.g., having the identical talents, the identical encoding scheme and comparable performance to permit them to stay dormant) point out that QuiteRAT has been derived from MagicRAT. Moreover, Cisco Talos notes that the final MagicRAT model they noticed was compiled in April 2022, whereas the QuiteRAT samples they discovered had been compiled in Might and July 2022. This may point out a swap from MagicRAT to QuiteRAT, which is smaller and extra compact: MagicRAT takes 18MB, whereas QuiteRAT is round 4MB to 5MB.
CollectionRAT
CollectionRAT is one other RAT used and doubtless developed by Lazarus. The malware is a packed Microsoft Basis Class library-based Home windows binary that decrypts and executes the precise malware code on the fly. The malware gathers data from the system it contaminated and offers completely different common features for a RAT: it permits knowledge assortment, can present a reverse shell to run arbitrary instructions on the system, learn and write on the disk, and obtain and execute extra payloads.
The researchers discovered data that may point out CollectionRAT has spawned from one other malware household referred to as EarlyRAT, which is attributed to the Andariel subgroup of Lazarus. One CollectionRAT pattern used the very same code-signing certificates as an older model of EarlyRAT from 2021.
DeimosC2
DeimosC2 is an open-source post-exploitation C2 software that leverages a number of communication strategies so as to management machines which were compromised. It’s utilized by Lazarus as a method of preliminary and chronic entry.
The researchers discovered a Linux DeimosC2 implant on the infrastructure, indicating the risk actor deliberate to deploy it in the course of the preliminary entry to compromised Linux-based servers. The implant was not closely personalized, which may be a sign that Lazarus continues to be within the technique of testing it or getting used to it.
The implants sometimes have numerous RAT capabilities, comparable to executing instructions, stealing credentials, downloading and executing extra payloads.
Malicious Plink
Plink, often known as PuTTY Hyperlink, is a respectable open-source software utilized by community directors to get reverse tunneling functionality when wanted. Lazarus used the software as-is previously, however the group has began to change the supply code of it to embed the reverse tunnel command strings within the binary itself.
Lazarus retains reusing the identical infrastructure
Though the group makes quite a lot of adjustments to its arsenal, the North Korean state-sponsored Lazarus risk actor “continues to make use of a lot of the identical infrastructure regardless of these parts being well-documented by safety researchers over time,” in response to Cisco Talos. That is excellent news for safety as a result of it permits IT employees and researchers to trace the risk actor extra simply and defend in opposition to it. But it may additionally imply that Lazarus is assured sufficient of their operations and don’t assume it’s needed to vary a lot of their assault infrastructure.
QuiteRAT has been present in the identical distant location as DeimosC2 brokers and MagicRAT malware used in 2022 by Lazarus. The placement has additionally been used for CollectionRAT.
The completely different instruments and malware utilized by Lazarus can all be tied collectively utilizing the infrastructure (Determine B).
Determine B
Learn how to defend your online business from this safety risk
On this assault marketing campaign, the preliminary compromise was finished by exploiting a vulnerability affecting Zoho’s ManageEngine ServiceDesk that was patched round November 2022. Ideas for safeguarding from this safety risk embody:
- Hold software program and working programs updated and patched.
- Monitor networks with safety options.
- Make guidelines to detect the communications from the malware uncovered on this assault marketing campaign.
- Monitor IP addresses utilized by the risk actor.
- Deploy safety options on endpoints and servers so as to detect malware and instruments that may be used to assault your group. These options also needs to monitor the e-mail contents, connected information and potential hyperlinks to malicious content material.
Disclosure: I work for Development Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.
[ad_2]