
[ad_1]

The flexibility to detect objects within the visible world is essential for pc imaginative and prescient and machine intelligence, enabling purposes like adaptive autonomous brokers and versatile procuring methods. Nonetheless, fashionable object detectors are restricted by the handbook annotations of their coaching information, leading to a vocabulary measurement considerably smaller than the huge array of objects encountered in actuality. To beat this, the open-vocabulary detection job (OVD) has emerged, using image-text pairs for coaching and incorporating new class names at check time by associating them with the picture content material. By treating classes as textual content embeddings, open-vocabulary detectors can predict a variety of unseen objects. Numerous methods akin to image-text pre-training, data distillation, pseudo labeling, and frozen fashions, usually using convolutional neural community (CNN) backbones, have been proposed. With the rising reputation of imaginative and prescient transformers (ViTs), you will need to discover their potential for constructing proficient open-vocabulary detectors.
The prevailing approaches assume the provision of pre-trained vision-language fashions (VLMs) and give attention to fine-tuning or distillation from these fashions to deal with the disparity between image-level pre-training and object-level fine-tuning. Nonetheless, as VLMs are primarily designed for image-level duties like classification and retrieval, they don’t absolutely leverage the idea of objects or areas throughout the pre-training section. Thus, it could possibly be helpful for open-vocabulary detection if we construct locality info into the image-text pre-training.
In “RO-ViT: Area-Conscious Pretraining for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Imaginative and prescient Transformers”, offered at CVPR 2023, we introduce a easy methodology to pre-train imaginative and prescient transformers in a region-aware method to enhance open-vocabulary detection. In imaginative and prescient transformers, positional embeddings are added to picture patches to encode details about the spatial place of every patch throughout the picture. Customary pre-training sometimes makes use of full-image positional embeddings, which doesn’t generalize nicely to detection duties. Thus, we suggest a brand new positional embedding scheme, known as “cropped positional embedding”, that higher aligns with using area crops in detection fine-tuning. As well as, we substitute the softmax cross entropy loss with focal loss in contrastive image-text studying, permitting us to be taught from tougher and informative examples. Lastly, we leverage current advances in novel object proposals to reinforce open-vocabulary detection fine-tuning, which is motivated by the commentary that present strategies usually miss novel objects throughout the proposal stage as a consequence of overfitting to foreground classes. We’re additionally releasing the code right here.
Area-aware image-text pre-training
Present VLMs are educated to match a picture as a complete to a textual content description. Nonetheless, we observe there’s a mismatch between the way in which the positional embeddings are used within the present contrastive pre-training approaches and open-vocabulary detection. The positional embeddings are essential to transformers as they supply the data of the place every aspect within the set comes from. This info is commonly helpful for downstream recognition and localization duties. Pre-training approaches sometimes apply full-image positional embeddings throughout coaching, and use the identical positional embeddings for downstream duties, e.g., zero-shot recognition. Nonetheless, the popularity happens at region-level for open-vocabulary detection fine-tuning, which requires the full-image positional embeddings to generalize to areas that they by no means see throughout the pre-training.
To handle this, we suggest cropped positional embeddings (CPE). With CPE, we upsample positional embeddings from the picture measurement typical for pre-training, e.g., 224×224 pixels, to that typical for detection duties, e.g., 1024×1024 pixels. Then we randomly crop and resize a area, and use it because the image-level positional embeddings throughout pre-training. The place, scale, and facet ratio of the crop is randomly sampled. Intuitively, this causes the mannequin to view a picture not as a full picture in itself, however as a area crop from some bigger unknown picture. This higher matches the downstream use case of detection the place recognition happens at region- slightly than image-level.
We additionally discover it helpful to be taught from laborious examples with a focal loss. Focal loss allows finer management over how laborious examples are weighted than what the softmax cross entropy loss can present. We undertake the focal loss and substitute it with the softmax cross entropy loss in each image-to-text and text-to-image losses. Each CPE and focal loss introduce no additional parameters and minimal computation prices.
Open-vocabulary detector fine-tuning
An open-vocabulary detector is educated with the detection labels of ‘base’ classes, however must detect the union of ‘base’ and ‘novel’ (unlabeled) classes at check time. Regardless of the spine options pre-trained from the huge open-vocabulary information, the added detector layers (neck and heads) are newly educated with the downstream detection dataset. Present approaches usually miss novel/unlabeled objects within the object proposal stage as a result of the proposals are inclined to classify them as background. To treatment this, we leverage current advances in a novel object proposal methodology and undertake the localization quality-based objectness (i.e., centerness rating) as a substitute of object-or-not binary classification rating, which is mixed with the detection rating. Throughout coaching, we compute the detection scores for every detected area because the cosine similarity between the area’s embedding (computed through RoI-Align operation) and the textual content embeddings of the bottom classes. At check time, we append the textual content embeddings of novel classes, and the detection rating is now computed with the union of the bottom and novel classes.
 |
| The pre-trained ViT spine is transferred to the downstream open-vocabulary detection by changing the worldwide common pooling with detector heads. The RoI-Align embeddings are matched with the cached class embeddings to acquire the VLM rating, which is mixed with the detection rating into the open-vocabulary detection rating. |
Outcomes
We consider RO-ViT on the LVIS open-vocabulary detection benchmark. On the system-level, our greatest mannequin achieves 33.6 field common precision on uncommon classes (APr) and 32.1 masks APr, which outperforms one of the best present ViT-based method OWL-ViT by 8.0 APr and one of the best CNN-based method ViLD-Ens by 5.8 masks APr. It additionally exceeds the efficiency of many different approaches based mostly on data distillation, pre-training, or joint coaching with weak supervision.
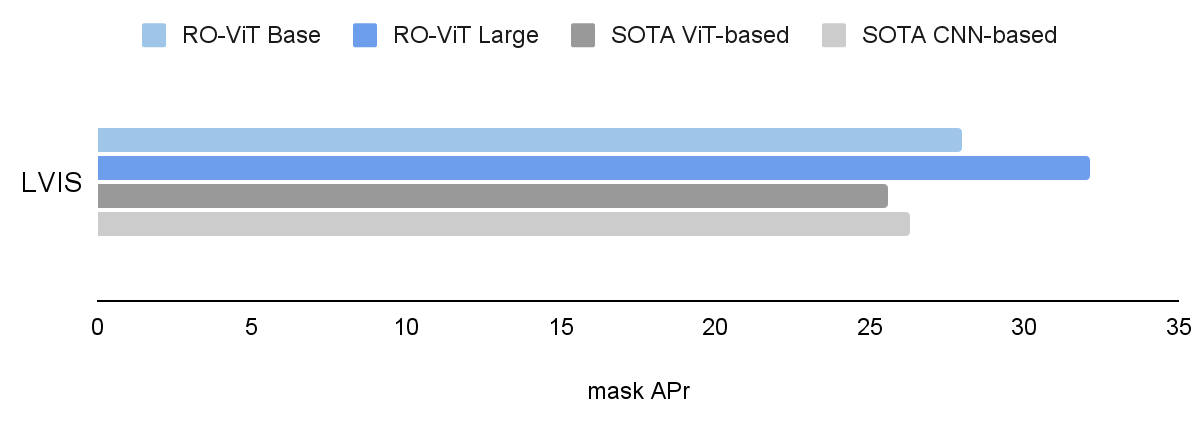 |
| RO-ViT outperforms each the state-of-the-art (SOTA) ViT-based and CNN-based strategies on LVIS open-vocabulary detection benchmark. We present masks AP on uncommon classes (APr) , aside from SOTA ViT-based (OwL-ViT) the place we present field AP. |
Other than evaluating region-level illustration via open-vocabulary detection, we consider the image-level illustration of RO-ViT in image-text retrieval via the MS-COCO and Flickr30K benchmarks. Our mannequin with 303M ViT outperforms the state-of-the-art CoCa mannequin with 1B ViT on MS COCO, and is on par on Flickr30K. This exhibits that our pre-training methodology not solely improves the region-level illustration but in addition the worldwide image-level illustration for retrieval.
 |
| We present zero-shot image-text retrieval on MS COCO and Flickr30K benchmarks, and examine with dual-encoder strategies. We report recall@1 (top-1 recall) on image-to-text (I2T) and text-to-image (T2I) retrieval duties. RO-ViT outperforms the state-of-the-art CoCa with the identical spine. |
Visualization of positional embeddings
We visualize and examine the discovered positional embeddings of RO-ViT with the baseline. Every tile is the cosine similarity between positional embeddings of 1 patch and all different patches. For instance, the tile within the top-left nook (marked in pink) visualizes the similarity between the positional embedding of the situation (row=1, column=1) and people positional embeddings of all different places in 2D. The brightness of the patch signifies how shut the discovered positional embeddings of various places are. RO-ViT varieties extra distinct clusters at completely different patch places displaying symmetrical international patterns across the middle patch.
Conclusion
We current RO-ViT, a contrastive image-text pre-training framework to bridge the hole between image-level pre-training and open-vocabulary detection fine-tuning. Our strategies are easy, scalable, and straightforward to use to any contrastive backbones with minimal computation overhead and no enhance in parameters. RO-ViT achieves the state-of-the-art on LVIS open-vocabulary detection benchmark and on the image-text retrieval benchmarks, displaying the discovered illustration isn’t solely helpful at region-level but in addition extremely efficient on the image-level. We hope this research can assist the analysis on open-vocabulary detection from the angle of image-text pre-training which might profit each region-level and image-level duties.
Acknowledgements
Dahun Kim, Anelia Angelova, and Weicheng Kuo performed this work and at the moment are at Google DeepMind. We want to thank our colleagues at Google Analysis for his or her recommendation and useful discussions.
[ad_2]


