[ad_1]
The peer-to-peer (P2) worm often known as P2PInfect has witnessed a surge in exercise since late August 2023, witnessing a 600x leap between September 12 and 19, 2023.
“This enhance in P2PInfect site visitors has coincided with a rising variety of variants seen within the wild, suggesting that the malware’s builders are working at a particularly excessive growth cadence,” Cado Safety researcher Matt Muir mentioned in a report revealed Wednesday.
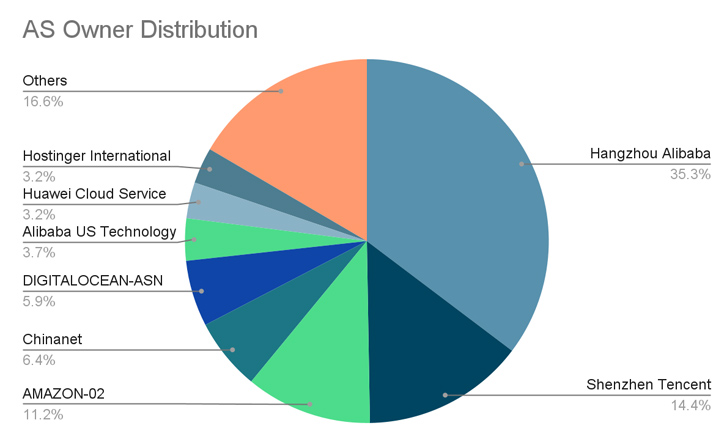
A majority of the compromises have been reported in China, the U.S., Germany, the U.Okay., Singapore, Hong Kong, and Japan.
P2PInfect first got here to mild in July 2023 for its potential to breach poorly secured Redis situations. The risk actors behind the marketing campaign have since resorted to totally different approaches for preliminary entry, together with the abuse of the database’s replication function to ship the malware.

Cado Safety mentioned it has noticed a rise in preliminary entry occasions attributable to P2PInfect by which the Redis SLAVEOF command is issued by an actor-controlled node to a goal to allow replication.
That is adopted by delivering a malicious Redis module to the goal, which, in flip, runs a command to retrieve and launch the primary payload, after which one other shell command is run to take away the Redis module from the disk in addition to disable the replication.
One of many new options of the newer variants is the addition of a persistence mechanism that leverages a cron job to launch the malware each half-hour.Moreover, there now exists a secondary methodology that retrieves a replica of the malware binary from a peer and executes ought to or not it’s deleted or the primary course of is terminated.
P2PInfect additional overwrites current SSH authorized_keys recordsdata with an attacker-controlled SSH key, successfully stopping current customers from logging in over SSH.
“The primary payload additionally iterates by all customers on the system and makes an attempt to alter their consumer passwords to a string prefixed by Pa_ and adopted by 7 alphanumeric characters (e.g. Pa_13HKlak),” Muir mentioned. This step, nevertheless, requires that the malware has root entry.
AI vs. AI: Harnessing AI Defenses In opposition to AI-Powered Dangers
Able to deal with new AI-driven cybersecurity challenges? Be a part of our insightful webinar with Zscaler to handle the rising risk of generative AI in cybersecurity.
Regardless of the rising sophistication of the malware, P2PInfect’s actual targets are unclear. Cado Safety mentioned it noticed the malware making an attempt to fetch a crypto miner payload, however there is no such thing as a proof of cryptomining up to now.
“It is clear that P2PInfect’s builders are dedicated to sustaining and iterating on the performance of their malicious payloads, whereas concurrently scaling the botnet throughout continents and cloud suppliers at a speedy fee,” Muir mentioned.
“It’s anticipated that these behind the botnet are both ready to implement further performance within the miner payload, or are aspiring to promote entry to the botnet to different people or teams.”
[ad_2]