
[ad_1]
Researchers on the Nationwide Heart for Supercomputing Purposes (NCSA) and The Grainger School of Engineering, College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), have made strides in stress prediction analysis utilizing synthetic intelligence. Their work, specializing in deep operator community (DeepONet) implementations, goals to enhance stress response predictions in advanced geometries, akin to these present in additive manufacturing. Using the NCSA’s Delta system, they’ve achieved considerably sooner outcomes in comparison with conventional finite component strategies.
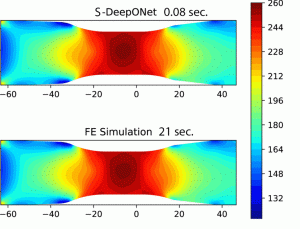
The staff performed their analysis via Illinois Computes, a program providing in depth computing and information storage assets. This initiative has facilitated collaboration throughout varied disciplines, combining machine studying and computational mechanics. The Delta system, famend for its high-performance GPU computing capabilities, was essential in coaching deep neural networks and producing coaching information utilizing Abaqus software program.
Two important publications have emerged from this analysis. The primary, in “Laptop Strategies in Utilized Mechanics and Engineering,” introduces a novel DeepONet utilizing a residual U-Internet (ResUNet) for encoding advanced geometries. This strategy marks the primary use of ResUNet in DeepONet structure, demonstrating superior reminiscence effectivity and suppleness over conventional strategies.
The second paper, revealed in “Engineering Purposes of Synthetic Intelligence,” describes one other revolutionary DeepONet model, S-DeepONet. It leverages superior sequential studying strategies, providing enhanced accuracy in multi-physics options beneath various thermal and mechanical masses.
“Additive manufacturing is a revolutionary manufacturing approach that opens practically limitless potentialities for its implementation,” mentioned mentioned Iwona Jasiuk, professor of mechanical science and engineering at UIUC..
“DeepONet serves as a robust and speedy computational instrument, which might simulate the additive manufacturing course of at varied spatial and temporal scales. Such simulations are wanted for deeper understanding of the additive manufacturing course of and its implementation and monitoring.”
This analysis isn’t just a leap in AI purposes but additionally holds important implications for superior manufacturing processes and the event of digital twins. The collaborative effort between NCSA and MechSE highlights the synergy of multidisciplinary experience and cutting-edge know-how.
Come and tell us your ideas on our Fb, X, and LinkedIn pages, and don’t neglect to join our weekly additive manufacturing e-newsletter to get all the newest tales delivered proper to your inbox.
[ad_2]