
[ad_1]
Generative AI can be utilized by attackers, however safety professionals should not lose sleep over it, in line with a Google Cloud risk intelligence analyst. Discover out why.
Google Cloud’s staff not too long ago spoke about probably the most notable cybersecurity threats of 2023 — multi-faceted extortion and zero-day exploitation — and predicted extra zero-day assaults in 2024, throughout two public, digital periods. Plus, Google predicts that each attackers and defenders will proceed to make use of generative AI. Nonetheless, generative AI most likely received’t create its personal malware in 2024.
Bounce to:
Two most notable cybersecurity threats of 2023
The 2 most notable cybersecurity threats of 2023, in line with Google Cloud’s Luke McNamara, principal belief and security analyst, have been multi-faceted extortion (often known as double extortion) and zero-day exploitation.
Multi-faceted exploitation
Multi-faceted exploitation consists of ransomware and knowledge theft, though the variety of ransomware assaults tracked by Google Cloud fell in 2023. The commonest ransomware households utilized in multi-faceted exploitation assaults have been LockBit, Clop and ALPHV.
Most ransomware assaults initially stemmed from stolen credentials. Brute pressure assaults and phishing have been the following most typical preliminary an infection vectors for ransomware.
SEE: Know the warning indicators if another person has accessed your Google account. (TechRepublic)
Attackers more and more put stolen credentials up on the market on knowledge leak websites, McNamara mentioned. “This previous quarter (Q3 2023) we noticed the very best variety of postings to DLS websites since we began monitoring this in 2020,” McNamara mentioned.
Many attackers are industry-agnostic, however “Quarter over quarter, manufacturing appears to be significantly hit and impacted disproportionately,” McNamara mentioned. “That’s the place we’re seeing plenty of the exercise when it comes to quantity.”
Zero-day exploitation
Zero-day exploitation is outlined by Google Cloud as vulnerabilities with no identified patches that risk actors are actively exploiting. In 2023, Google Cloud Safety tracked 89 such assaults (Determine A), surpassing the earlier excessive of 2021.
Determine A
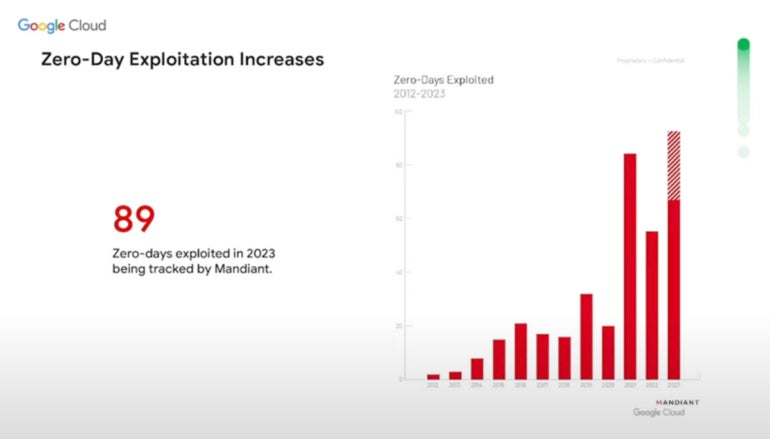
Many zero-day threats are nation-state affiliated or sponsored. The second most typical motivation amongst risk actors utilizing zero-day threats is to amass cash.
SEE: What the Cisco Talos 12 months in Evaluation report revealed (TechRepublic)
Google Cloud’s 2024 cybersecurity forecast
Andrew Kopcienski, principal risk intelligence analyst at Google’s Mandiant Communication Heart, talked about nation-state risk actors, zero-day assaults, motion between cloud environments and credential theft throughout his presentation about cyber threats in 2024. Specifically, China and Russia are specializing in zero-day assaults, he mentioned.
“We absolutely count on to see much more zero day use in 2024 by not simply nation-state sponsored attackers however cyber criminals as effectively,” mentioned Kopcienski. “Zero days are top-of-the-line strategies attackers have to stay undetected as soon as they get right into a community.”
China-sponsored risk actors
China-sponsored actors have centered on creating capabilities to find and utilizing zero days and botnets to stay undetected, Kopcienski mentioned. Google Cloud expects China’s cyber risk efforts to give attention to high-tech fields like chip improvement.
Russian-sponsored espionage
Russian espionage centered on Ukraine has been an issue, he mentioned. Google Cloud discovered Russia has performed campaigns exterior Ukraine as effectively, however these largely give attention to gaining strategic data concerning Ukraine, Kopcienski mentioned. Russian-sponsored attackers use “residing off the land” assaults that don’t require malware; as an alternative, they abuse native capabilities, and their visitors appears to be like like native visitors. Google Cloud expects extra assaults from Russian-backed actors in 2024, largely centered on victims inside Ukraine or associated to Ukraine.
North Korean-sponsored risk actors
Google Cloud additionally regarded intently at nation-state actors related to North Korea.
“They’ve developed a scrappy functionality to launch software program provide chain assaults,” Kopcienski mentioned.
North Korea was the primary identified nation-state actor to make use of “cascading” software program provide chain assaults, which piggybacked off one another. Many of those assaults are about stealing cryptocurrency or firms conducting cryptocurrency operations. Google Cloud expects to see North Korea-affiliated risk actors’ assaults broaden in 2024.
Credential theft and extortion
One other concern for 2024 is extortion. “Credential theft (Determine B) is the secret … that has grow to be probably the most drastic and hottest measure plenty of these attackers are utilizing,” Kopcienski mentioned.
Determine B
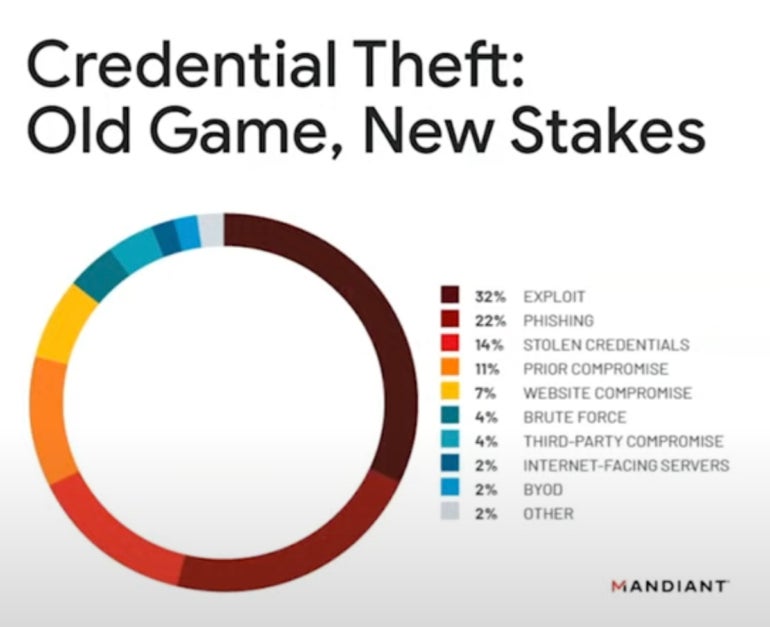
“Into 2024, we count on to see a give attention to knowledge leak websites, particularly by extortion actors,” he mentioned.
Motion between cloud environments
Attackers in 2024 could use techniques, methods and procedures that enable them to journey throughout totally different cloud environments, probably as a result of rising use of cloud and hybrid environments.
How generative AI has and can have an effect on cybersecurity in 2023 and 2024
Attackers can use generative AI to create textual content, voice messages and imagery, and Google Cloud expects this to grow to be extra frequent.
“AI is enabling specific sorts of malicious attackers, largely in disinformation campaigns. We’re very involved going into subsequent 12 months in regards to the affect of disinformation that has been augmented by AI, particularly with regards to the 2024 election,” mentioned Kopcienski.
In 2023, generative AI has been utilized by attackers and defenders. In 2024, AI could also be used to extend the dimensions of assaults, comparable to by adopting AI in name facilities working ransomware negotiations.
Generative AI would possibly have the ability to create malware sooner or later sooner or later, however Kopcuenski mentioned to not count on that to occur as quickly as 2024. He recommends cybersecurity professionals “stay grounded” and never lose sleep with regards to generative AI. A lot of its threats are “hypothetical,” he mentioned.
“There’s plenty of hype and disinformation on the market already about what AI can and may’t do. … (AI is) not an awesome revolution when it comes to the threats being posed,” he mentioned.
[ad_2]