[ad_1]
Sophos X-Ops is warning the hospitality trade {that a} marketing campaign concentrating on lodges worldwide with password-stealing malware is utilizing emailed complaints about service issues or requests for data as a social engineering lure to realize the belief of the marketing campaign’s targets, earlier than sending them hyperlinks to malicious payloads.
The attackers are utilizing a technique just like the one Sophos X-Ops uncovered within the months main as much as the US federal tax submitting deadline in April 2023: They initially contact the goal over electronic mail that accommodates nothing however textual content, however with material a service-oriented enterprise (like a resort) would wish to reply to shortly. Solely after the goal responds to the risk actor’s preliminary electronic mail does the risk actor ship a followup message linking to what they declare is particulars about their request or grievance.
The social engineering angle spans all kinds of material, however may be categorized into two generalized buckets: complaints about critical points the sender claims to have skilled in a current keep, or requests for data to assist with a possible future reserving.
Sophos X-Ops has already briefed representatives of the Retail and Hospitality Info Sharing and Evaluation Middle (RH-ISAC) about this assault concentrating on their trade in the course of the busy end-of-year vacation journey season.
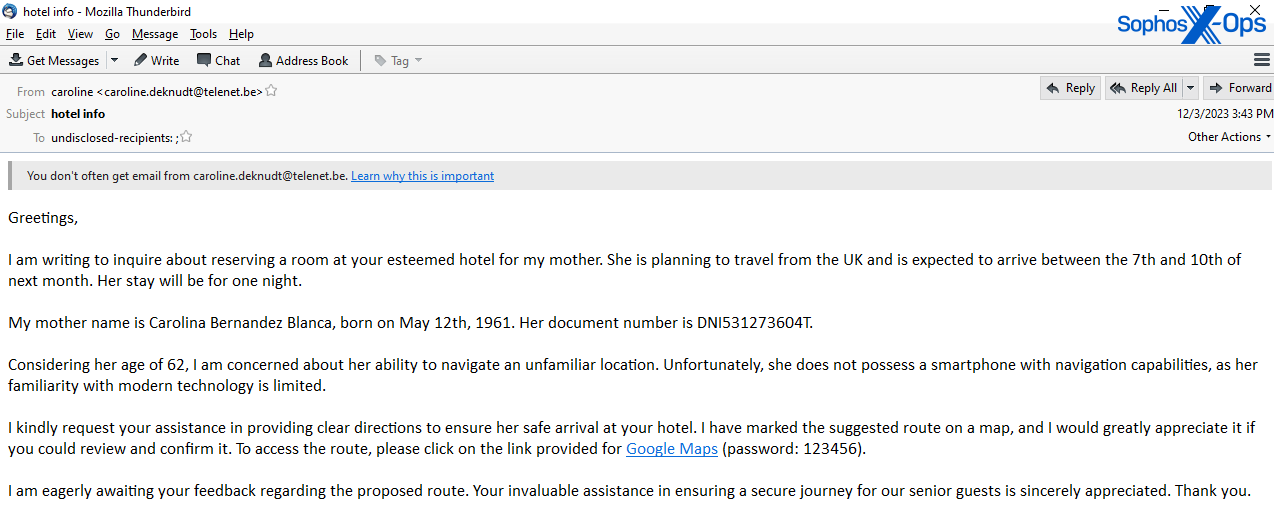
I’m writing to inquire
The content material of the ‘grievance’-style messages vary from allegations of violent assaults or bigoted conduct by members of the resort workers, to assertions that the “visitor” had gadgets stolen or misplaced from their room. The ‘requests for data’-type messages included emails asking for lodging for somebody with extreme allergy symptoms, messages about how the resort may assist a enterprise assembly, or inquiries about accessibility throughout the resort for a disabled or aged visitor.
In each case, as soon as a consultant from the resort responded to the preliminary inquiry asking for extra data, the risk actor replied with a message that – the attacker claims – hyperlinks to documentation or proof supporting their claims or requests. The “documentation” is just not precise documentation, however the malware payload, wrapped in a password-protected archive file.
The hyperlinks level to public cloud storage companies, resembling Google Drive, and the physique of the message accommodates a password (normally numeric) that the recipient is prompted to make use of to open the Zip or Rar archive on the different finish of the obtain hyperlink.
Widespread traits of electronic mail messages within the marketing campaign
The messages attackers ship to resort workers share some traits that make them extra suspicious and benefit extra warning by recipients.
Like many profitable malspam campaigns, the messages are engineered to play on feelings and on the goal’s want to render help – a self-selecting trait for profitable individuals working within the hospitality trade.
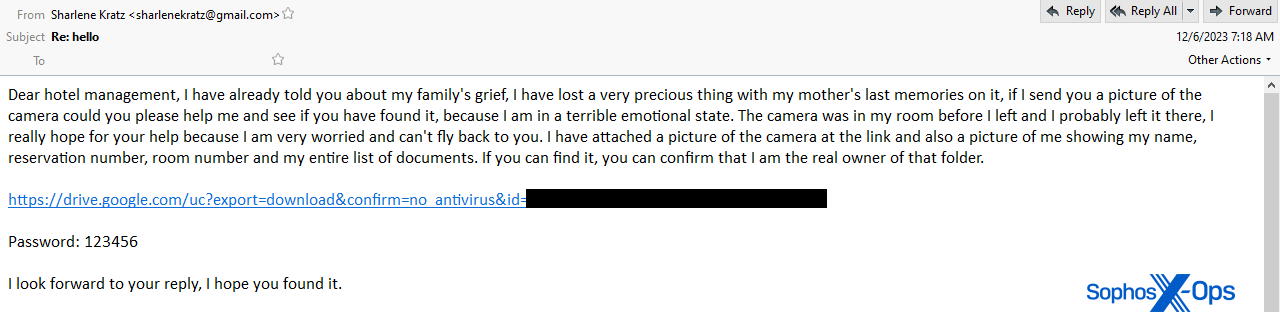
In a single instance, the risk actor tells a resort staffer that they left a digicam behind in a room that accommodates images of a just lately deceased relative, and asks the resort for assist finding the digicam.
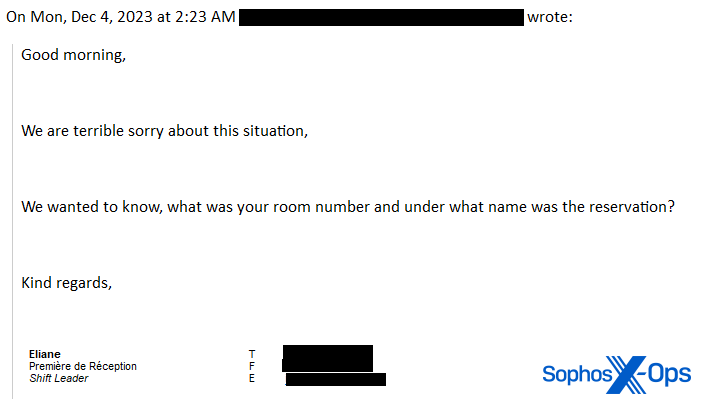
When the resort workers replied, asking for the room quantity and title the reservation was underneath, the risk actor replies, feigning exasperation.
“I’ve already advised you about my household’s grief, I’ve misplaced a really treasured factor with my mom’s final reminiscences on it, if I ship you an image of the digicam may you please assist me” together with a hyperlink to a file hosted on Google Drive, and the textual content “Password: 123456” beneath the hyperlink.
In one other instance, the risk actor emails a resort and asks them to answer as a result of they “have been unable to contact you thru the web site or by cellphone.” When the reserving agent from the resort asks them to supply extra particulars about their plans, the risk actor replies, claiming they’ve booked rooms by means of the web site however have to make preparations for the lodging of a member of the family with a incapacity. Their second electronic mail hyperlinks to a zipper file hosted on Google Drive they declare accommodates “medical information and physician’s suggestions” and, once more, a password of 123456 wanted to open the file.
In that message, the risk actor provides the next “My husband talked about that this Google Drive hyperlink could solely be suitable with Home windows computer systems. The doc holds very important particulars, together with our reserving quantity and proof of cost. It’s important to familiarize your self with these particulars.”
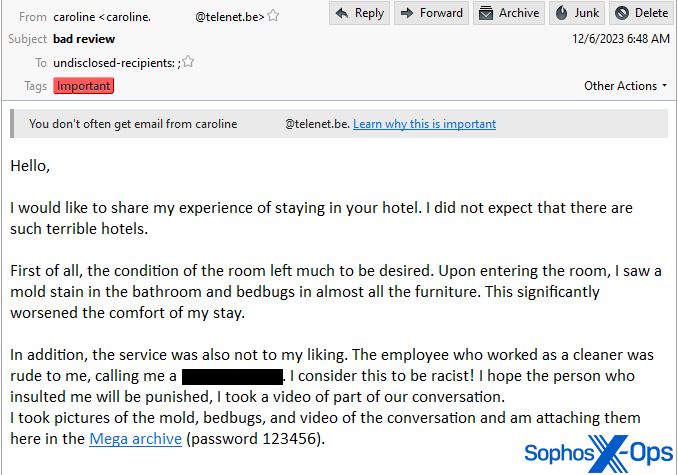
In what is perhaps probably the most egregious instance, the risk actor requested for contact with a supervisor to deal with an issue that they had on the resort. As soon as the supervisor replies, the risk actor writes “I didn’t count on there are such horrible lodges,” describing a horrifying (fictitious) expertise that included mouldy partitions, “bedbugs in nearly all of the furnishings” that “considerably worsened the consolation of my keep,” and an worker who used a racist epithet. The e-mail hyperlinks to a RAR archive file hosted on the Mega.nz cloud internet hosting supplier, additionally with a password of 123456, that the sender alleges accommodates a video of the confrontation between the visitor and workers member.
The emails all contrive an excuse to share documentation with the resort employees by way of cloud storage, from Google Drive, Mega.nz, Dropbox, or from an handle within the content material internet hosting area of the chat platform Discord. The malicious payloads linked from these messages have been compressed in both the Zip or Rar compression format, and used one of many following checklist of passwords.
- 1111
- 123456
- 2023
- info2023
- resort
- 501949
We noticed many extra examples of inventive writing by the risk actor. Emails complained about friends contracting quite a lot of illnesses; considerations over allergic reactions to cleansing merchandise; allegations of being poisoned within the resort; stains on mattresses, partitions, or in loos; bugs on furnishings within the rooms; purses, rings, costly watches or cameras being left behind or stolen from rooms; a necessity for lodging or help for friends with restricted mobility or entry to expertise; and impolite, violent, or bigoted conduct by workers directed on the visitor.
Payloads designed to evade sandboxing
The malware payloads themselves have been created with the intent to make it tougher to scan or detect the malicious content material.
The archives are all password-protected, which prevents the cloud service internet hosting them from casually scanning the contents and detecting whether or not the payload is malicious.
When unpacked from their archive containers, the malware itself has traits that additionally assist it elude quick detection.
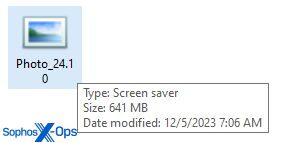
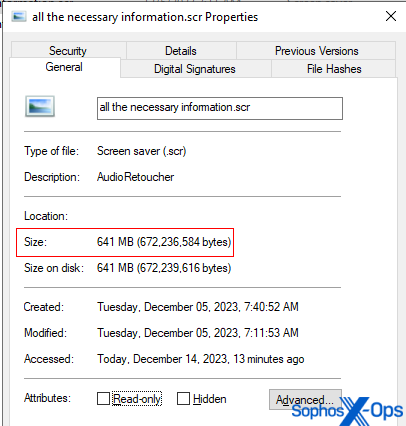
Lots of the unzipped or de-archived payload information are vastly bigger than a typical executable. A number of of the samples we uncovered weigh in at properly above 600MB in measurement. Information of this measurement is perhaps missed by static endpoint safety scanners designed to course of a lot smaller information.
 The overwhelming majority of the interior content material of these information was simply bytes containing zeroes, used as space-filler.
The overwhelming majority of the interior content material of these information was simply bytes containing zeroes, used as space-filler.
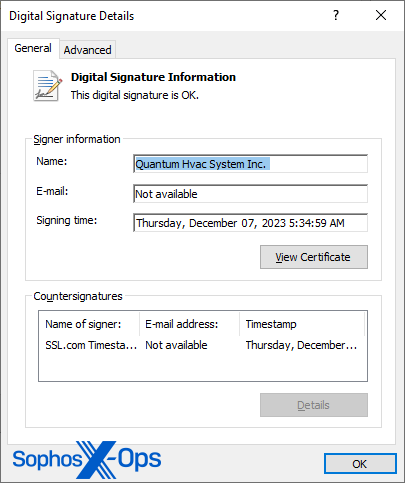
Practically all the samples have been signed with a code-validation certificates. Lots of the certificates are model new – obtained in the course of the course of the marketing campaign’s operational interval – and queries of a few of these certificates point out the signature stays legitimate for most of the samples, whereas others look like faked or counterfeit, and don’t move validation.
Some endpoint safety instruments will routinely exclude executables with legitimate signatures from scanning; Some will solely search for the presence of a certificates, not bothering to test whether or not it’s legitimate.
Easy however efficient password-stealer malware
Many of the samples look like variants of a malware household variously referred to as Redline Stealer or Vidar Stealer. Regardless of their measurement, 99% of the quantity of the malware executables (with both an .exe or .scr extension) which might be higher than 600MB in measurement are simply zeroes. The malware code is tacked on to the tip of the very massive information with soar instructions that leap over the empty area.
When executed, the malware instantly connects to a URL on the Telegram encrypted messaging service. The URL factors to a chat room, the title of which is an online handle used for the bot’s command-and-control. On the time we examined this malware, the C2 handle was an IP handle and a high-numbered, nonstandard TCP port.
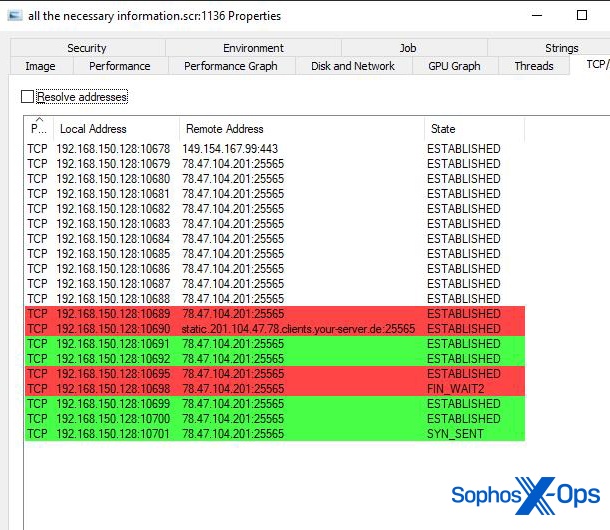 The bot then connects to the handle it retrieves from the Telegram channel and downloads a payload able to quite a lot of options from that handle. It makes use of HTTP POST requests to the C2 server to submit telemetry concerning the contaminated machine, together with particulars of account data saved within the browser and screenshots of the desktop. The server delivers data the bot can use to encrypt its communication in response.
The bot then connects to the handle it retrieves from the Telegram channel and downloads a payload able to quite a lot of options from that handle. It makes use of HTTP POST requests to the C2 server to submit telemetry concerning the contaminated machine, together with particulars of account data saved within the browser and screenshots of the desktop. The server delivers data the bot can use to encrypt its communication in response.
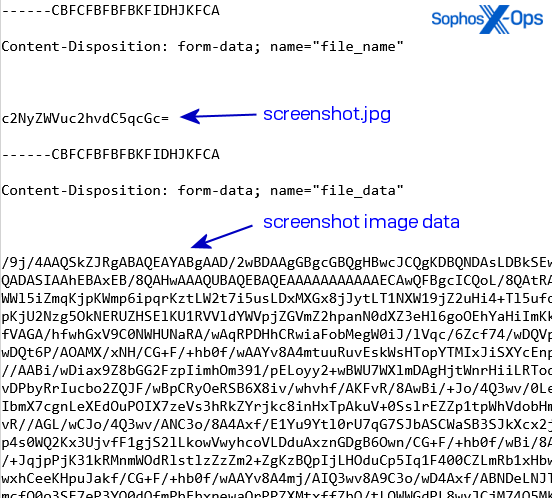 The malware doesn’t set up persistence on the host machine. It runs as soon as, does its work extracting then exfiltrating the info it needs to steal, then quits. Along with passwords and cookie data, the bot profiles the machine it’s operating on, and sends every thing about it to the bot controller. The samples we ran didn’t even delete themselves after operating.
The malware doesn’t set up persistence on the host machine. It runs as soon as, does its work extracting then exfiltrating the info it needs to steal, then quits. Along with passwords and cookie data, the bot profiles the machine it’s operating on, and sends every thing about it to the bot controller. The samples we ran didn’t even delete themselves after operating.
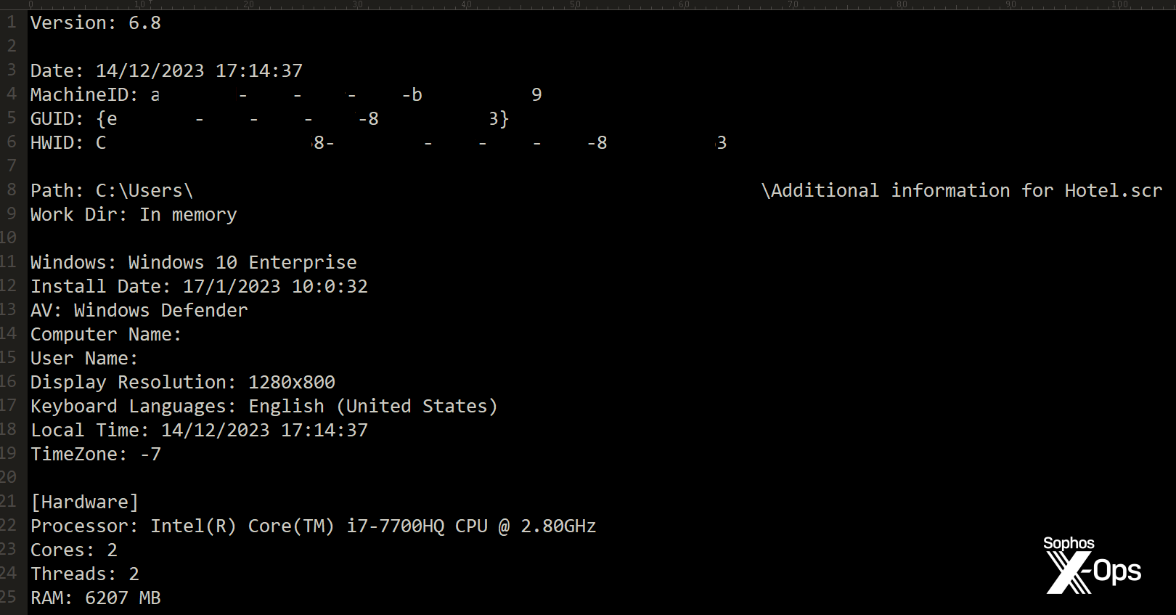 On the time of this writing, Sophos X-Ops has retrieved greater than 50 distinctive samples from cloud storage the place the information have been hosted by the risk actors conducting this marketing campaign. We’ve additionally reported the malicious hyperlinks to the assorted cloud storage suppliers internet hosting the malware. Most of these samples displayed few-to-no detections in Virustotal.
On the time of this writing, Sophos X-Ops has retrieved greater than 50 distinctive samples from cloud storage the place the information have been hosted by the risk actors conducting this marketing campaign. We’ve additionally reported the malicious hyperlinks to the assorted cloud storage suppliers internet hosting the malware. Most of these samples displayed few-to-no detections in Virustotal.
Sophos has revealed indicators of compromise to our Github repository.
Sophos endpoint safety merchandise will detect the malware as Troj/Agent-BKJE. Makes an attempt to exfiltrate credentials are blocked utilizing the behavioral detection Creds_2D.
Acknowledgments
Sophos X-Ops thanks Senior Menace Researchers Felix Weyne and Anand Ajjan for recognizing the marketing campaign in its early phases and elevating the alarm, and workers on the RH-ISAC for his or her assist disseminating warnings about this assault to their members and the resort trade at massive.
[ad_2]