
[ad_1]
With ultra-low energy consumption and decreased manufacturing prices, this growth guarantees to redefine the panorama of reminiscence options and pave the best way for next-generation AI {hardware}.
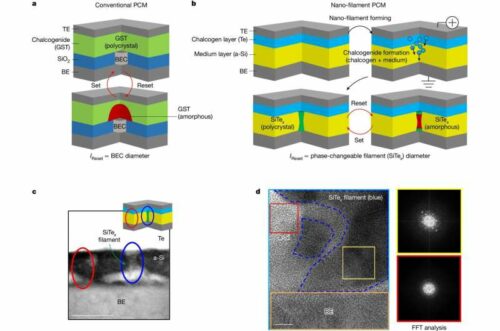
A group of researchers from KAIST’s Faculty of Electrical Engineering, led by Professor Shinhyun Choi, has launched a brand new phase-change reminiscence system poised to revolutionize the sphere of reminiscence know-how and neuromorphic computing. This innovation is distinguished by its ultra-low energy consumption and low processing prices, making it a powerful candidate to exchange present reminiscence options like DRAM and NAND flash reminiscence.
Conventional part change reminiscence units, whereas providing the advantages of each DRAM’s velocity and NAND flash reminiscence’s non-volatility, have been hindered by their excessive energy calls for and dear manufacturing processes, significantly when scaled down. These challenges have restricted their utility in creating sensible large-capacity reminiscence merchandise or within the growth of neuromorphic methods, which goal to imitate the human mind’s performance.
Addressing these crucial points, Professor Choi’s group has efficiently engineered an ultra-low–energy part change reminiscence system by an revolutionary methodology. This strategy entails electrically forming a nanometer-scale part changeable filament, bypassing the necessity for costly and sophisticated fabrication processes related to conventional strategies. Remarkably, this system operates with 15 occasions much less energy than its predecessors fabricated utilizing subtle lithography instruments.
The importance of this development extends past its rapid sensible functions. By merging the velocity of DRAM with the non-volatile nature of NAND flash reminiscence, part change reminiscence is rising as a number one resolution for future reminiscence and computing applied sciences. This new system, particularly, opens the door to high-density three-dimensional vertical reminiscence architectures and neuromorphic computing methods, providing a flexible platform for exploring a variety of supplies.
The group is optimistic in regards to the potential of this analysis to put the groundwork for future developments in digital engineering. With its promise of considerably decreased manufacturing prices and enhanced power effectivity, this part change reminiscence system is predicted to pave the best way for revolutionary functions within the realms of storage and computing, marking a big step ahead within the quest for next-generation AI {hardware}.
[ad_2]

