
[ad_1]
Anthony Perry and Addison Whitney coauthored this report.
As expertise continues to develop at a speedy tempo, nation states and unaffiliated people alike are swiftly creating new malicious pc viruses to search out vulnerabilities in pc techniques and obtain their political and private goals. To guard towards these assaults, cybersecurity corporations use quite a lot of strategies to detect malware (malicious code) from getting into their techniques. Present malware detection techniques consider components in a file or consider the file as an entire. New analysis exhibits that different avenues for malware detection exist, particularly, by breaking apart the file into sections after which evaluating the ensuing components. This weblog publish explains how our staff developed an method that may take a group of recognized malware recordsdata and use their part hashes to determine and analyze different candidate recordsdata in a malware repository.
Earlier than describing this analysis, we want to outline some key phrases:
- A hash is a perform that converts an enter to a singular output of a set size. This course of is repeatable and can produce the identical output when given the identical. As well as, these features are “a technique,” which means that it is vitally onerous to search out the enter worth given a hash perform’s output. We primarily centered on hashing two forms of info for this evaluation: file hashes and part hashes.
- A file hash is the output of a hash perform when given the whole lot of a file. For our functions, any two recordsdata which have the identical file hash are equivalent.
- A part hash is the output of a hash perform, the place the enter is a given part of a conveyable executable (PE), which is a standardized file format used to ship executable recordsdata (comparable to .exe and .dll) for packages based mostly on the Microsoft working system. These recordsdata include sections, the place every part is a primary unit of code or knowledge. For instance, some frequent sections discovered inside a PE file are
- .textual content used to retailer code
- .knowledge used to retailer knowledge
- .rsrc for useful resource
Whereas every part is vital for this system to execute correctly, we’re primarily within the relationship between recordsdata that include equivalent sections, which can point out code reuse.
Previous Analysis in Part Hash Evaluation
In 2019, Ian Shiel and Stephen O’Shaughnessy researched the potential of utilizing part hashes as a way to determine malware. They famous that almost all malware isn’t distinctive, however merely a variant of an overarching malware household. In altering just some characters within the malware supply code, the file hash could be completely completely different, even when 99.8 p.c of the remaining code matched the unique model. In coordination with a business malware repository, Shiel and O’Shaughnessy created a pipeline that hashed and matched malware households by their part hashes. When analyzing 96 GB value of malware, and utilizing the best-performing outcomes of every methodology, the section-level methodology leads to 92 p.c extra true positives for non-obfuscated malware and 88 p.c extra for obfuscated malware.
We determined to check their method with our personal knowledge by evaluating this technique with a particular candidate piece of malware to find out if we may use the part hashes to search out different candidate recordsdata. We selected HermeticWiper because the take a look at as a result of it was an lively piece of malware with reporting from a number of sources.
Dependencies for Part Hash Evaluation of Candidate Information
To assist determine code reuse with HermeticWiper, we used a number of instruments:
- Pharos, an open-source device developed by SEI, was used to acquire file hashes.
- A malware repository supplied by SEI that gave us entry to malware info (nevertheless, part hash evaluation isn’t restricted to this particular system).
- Python, which we used to
- work together with the malware repository database
- create histograms that may be graphed in packages like Excel
- create graphical output
- We additionally used publicly out there hashes of HermeticWiper and different malware focused at Ukraine.
A Methodology For Part Hash Evaluation
After the preliminary malware hashes have been recognized, the code will pull the related file info from the repository, together with every file’s MD5 hash, part hashes, sort, and dimension. Different attributes of the file should not wanted for the present evaluation.
Every file’s info is saved after it has been loaded. Every file’s part hashes are queried on the database to gather new file hashes that share the preliminary part hashes. This step is extremely vital, as a result of it eliminates all gaps in our preliminary assortment. It additionally helps present relationships between malware households. Our script improves previous analysis because the file’s hashes are downloaded solely from the repository, which is far safer as a result of no malware is downloaded onto the consumer’s pc.
Having run all the question, we then graphed the connection between hash sections and their recordsdata. With out a lot effort in the course of the evaluation interval, we are able to present a visible diagram of those relationships. Determine 1 highlights the part hash relationships of HermeticWiper. The Authentic Information are rectangles which are mild inexperienced, these recordsdata are linked to the part hashes that are represented as ovals. The blue ovals are DATA sections, the magenta ovals are TEXT sections, the yellow ovals are empty part hashes, and the orange ovals are overlay sections with crypto info in them. Determine 1 exhibits two clusters of candidates which have two tied to at least one Textual content part and the opposite three sharing a separate TEXT part.
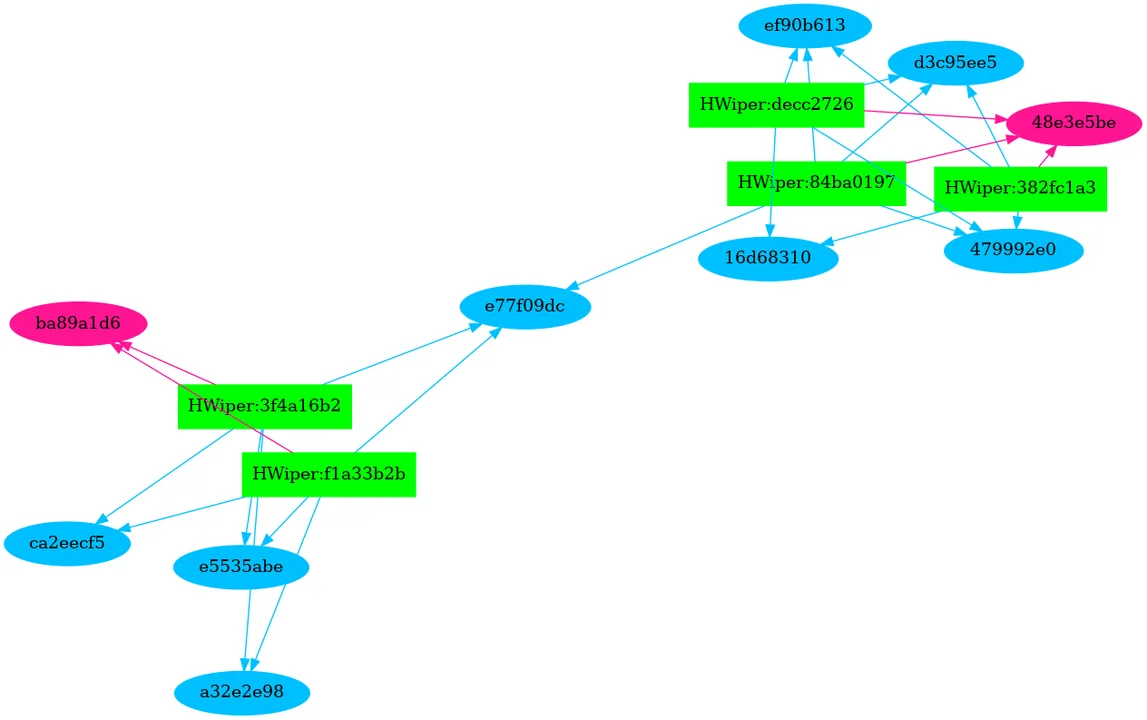
Determine 1 – Airtight Wiper Part Hash Evaluation
Utilizing Part Hashes to Establish Associated Malware Candidates
The ensuing piece of software program leverages part hashes to determine different items of malware. This software program has proven us recordsdata that won’t have been recognized beforehand as a part of the household. Within the ensuing picture, Determine 2 beneath, the brand new recordsdata are proven as darkish olive-green rectangles and all newly recognized recordsdata within the HermeticWiper cluster have been certainly malicious. The software program additionally doesn’t want elevated permissions to work or entry to the malware itself. All of the storage and processing might be carried out by the server, leaving analysts extra time to deal with the upper degree evaluation. General, for our HermeticWiper file, processing took solely a matter of minutes.
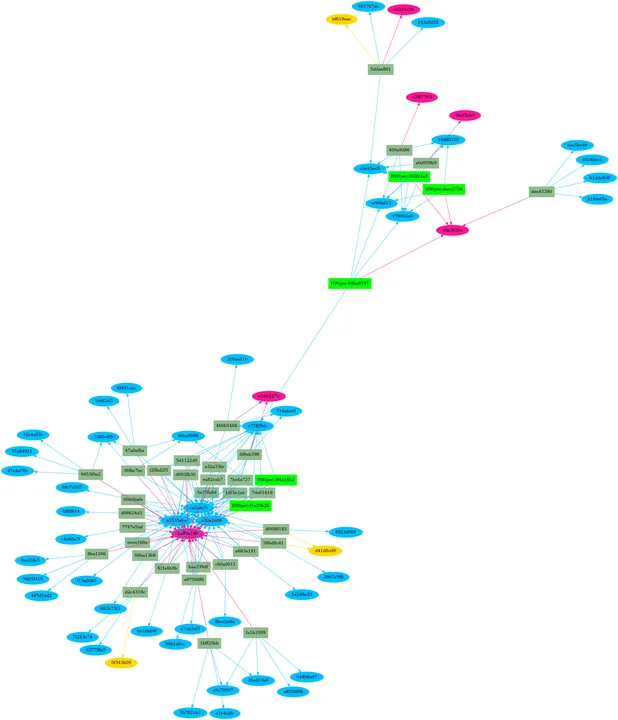
Determine 2 – HermeticWiper Part Hash Growth
Future Work in Previous Part Hashes of Malware Candidates
We’re seeing that many features are additionally shared between items of malware. The subsequent step is to make use of the same course of for perform hashes, which offers extra technique of figuring out code similarities between candidate software program samples. This course of can act as a validation and refinement of the part hash similarity evaluation. In our HermeticWiper case research, Determine 2 exhibits we have now two clusters of recordsdata: 30 recordsdata sharing the identical TEXT part and 4 recordsdata sharing a distinct TEXT. The 2 clusters share 95 p.c of their codebase, which signifies that they’re associated and probably replicate two completely different variations of the identical utility.
We’ve got noticed important clustering round our malware samples, indicating the opportunity of auto-classifying malware. Primarily based on the part or perform traits, if a majority of the part hashes match with a malicious household, it may be defended towards with none in-depth evaluation. This type of evaluation will pressure attackers to take a position considerably within the growth course of. Every perform and part have to be distinctive, which requires expending extra assets for every iteration, relatively than making incremental enhancements over time.
We additionally have to take care of unpacking and different types of obfuscation, which can all the time current an issue when combating malware builders. Including capabilities into the device to auto-detect and remediate obfuscation would enable our course of to satisfy increased ranges of success, by evaluating content material and never encrypted blobs.
Automated file-section hash evaluation can considerably velocity up evaluation, as a result of we have now proved with a group of hashes that we are able to determine executables by shared options with no important funding of effort. This device additionally highlights some fascinating makes use of for the malware repository that haven’t been explored beforehand. Whereas the work we did supplied a proof of idea to the SEI Malware Household Evaluation (MFA) staff, we’re excited about increasing its capabilities for sooner evaluation that doesn’t require downloading malware samples. Whereas our device is rudimentary at current, it has the potential to grow to be a a lot bigger and complex software program suite.
[ad_2]