[ad_1]
In at this time’s world, the Web of Issues (IoT) refers to a community the place billions of bodily gadgets are linked to the web. Not solely are there billions of gadgets already linked, however the variety of linked gadgets can be rising by billions yearly.
To help this huge variety of IoT gadgets, a strong infrastructure is required to deal with the transaction of all the information. This infrastructure is supplied by IoT cloud platforms akin to Ubidots, IFTTT, Blynk, ThingSpeak, Particle Cloud, and others. Nonetheless, on this tutorial, we shall be specializing in the Arduino IoT Cloud platform. Why? You would possibly ask. To me, the pricing is cheap, the interface is clear, and it’s feature-rich. So, with out additional ado, let’s dive proper into it.
What’s the Arduino IoT cloud?
The Arduino IoT Cloud is a platform for IoT gadgets and functions. It facilitates connecting Arduino gadgets to the web, knowledge assortment, distant management, and automation. Customers can management gadgets, create automation and extra. It’s designed for ease of use, even for non-technical customers.
How does Arduino IoT cloud work?
The Arduino IoT Cloud lets you register and program your Arduino gadget, create a ‘Factor’ with properties, widgets, and actions, after which monitor, management, and automate your gadget from the dashboard. It additionally supplies APIs for integration with different companies.
Options of Arduino IoT Cloud
From pre-built Templates to internet hook APIs there are a ton of options that the Arduino IoT cloud has to supply, all of these options are listed under.
- Knowledge Monitoring – discover ways to simply monitor your Arduino’s sensor values by means of a dashboard.
- Variable Synchronization – variable synchronization lets you sync variables throughout gadgets, enabling communication between gadgets with minimal coding.
- Scheduler – schedule jobs to go on/off for a selected period of time (seconds, minutes, hours).
- Over-The-Air (OTA) Uploads – add code to gadgets not linked to your laptop.
- Webhooks – combine your challenge with one other service, akin to IFTTT.
- Amazon Alexa Help – make your challenge voice managed with the Amazon Alexa integration.
- Dashboard Sharing – share your knowledge with different folks around the globe.
Record of Arduino Cloud Supported Units
To make use of the Arduino IoT cloud platform you will must must have a cloud appropriate Arduino board. For you could select an official Arduino board or a 3rd get together board based mostly on the ESP32 / ESP8266 microcontroller. All of the supported boards are listed under.
The next boards connect with the Arduino IoT Cloud through Wi-Fi.
- MKR 1000 Wi-Fi
- MKR Wi-Fi 1010
- Nano RP2040 Join
- Nano 33 IoT
- GIGA R1 Wi-Fi
- Portenta H7
- Portenta H7 Lite Related
- Portenta Machine Management
- Nicla Imaginative and prescient
- Opta.
Aside from that the Arduino IoT Cloud additionally helps LoRa WAN through The Issues Stack and it additionally helps GSM and NB-IoT boards just like the MKR GSM 1400 and MKR NB 1500 aside from that it additionally helps GSM and NB-IOT Boards like MKR GSM 1400 and it has help for ESP32 and ESP8266.
Configuring the Arduino IOT Cloud
Organising the Arduino Cloud is simple and easy, let’s check out the right way to go from begin to end!
- Creating an Arduino Account
To begin utilizing the Arduino IoT Cloud, it’s essential to have an Arduino account. If you do not have one, you have to to create one.
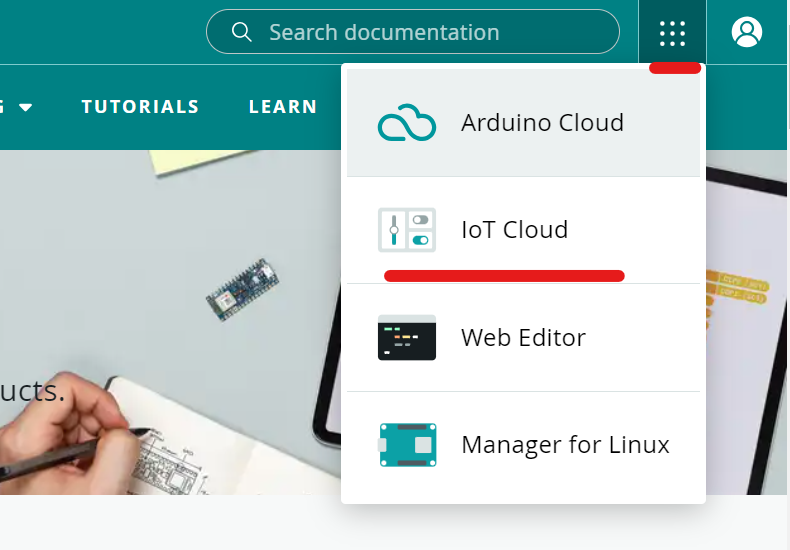
- Go to the Arduino IoT Cloud
Now click on on the dotted field formed menu icon, and click on on IoT Cloud. You too can go on to the Arduino IoT Cloud, by clicking on the hyperlink.
- Creating A Factor
Now it’s essential to create a Factor. A Factor is a linked gadget that may talk with the cloud. You may make your Issues work together with different Issues or anything within the bodily world. To get began it’s essential to click on on the Create Factor button.
Right here it’s essential to do 4 issues, first it’s essential to title your Factor. Naming a factor will make it straightforward so that you can discover the gadget later.
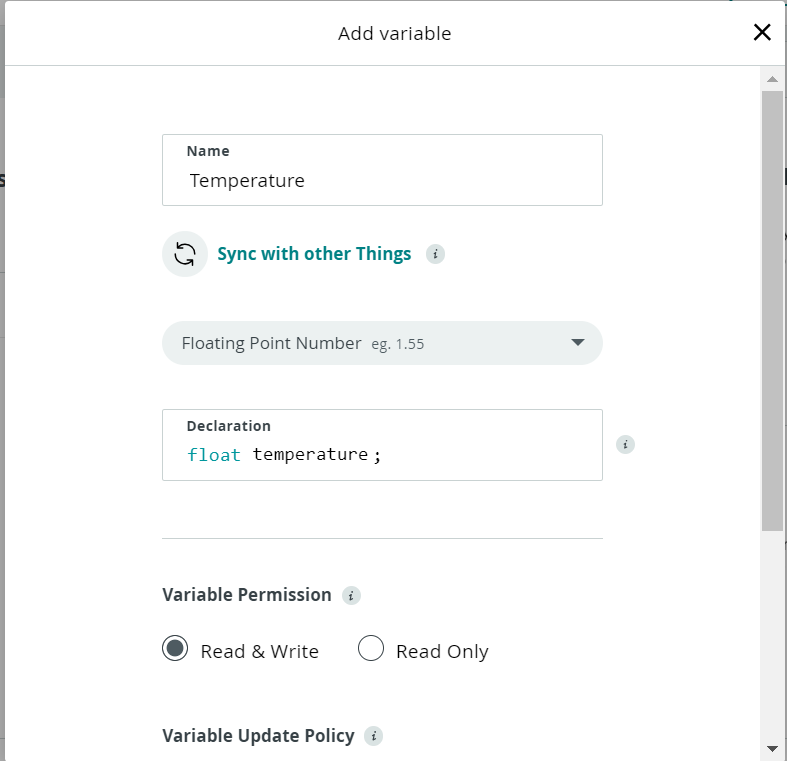
Now , it’s essential to click on on the Add variable and you’ll be offered with the above window , the place it’s essential to give a reputation to the variable. We named our variable led and on the Choose variable dropdown now we have chosen the Alexa appropriate and Primary sort variable. Now for the variable sort now we have chosen mild. Lastly as for the Variable Permission we’ll choose Learn & Write and for the Variable Replace Coverage we’ll choose on change. And we’ll save the variable.
The subsequent variable is for Temperature. We are going to give the title for the variable and we’ll set the variable sort as float. And we’ll do the identical for humidity.
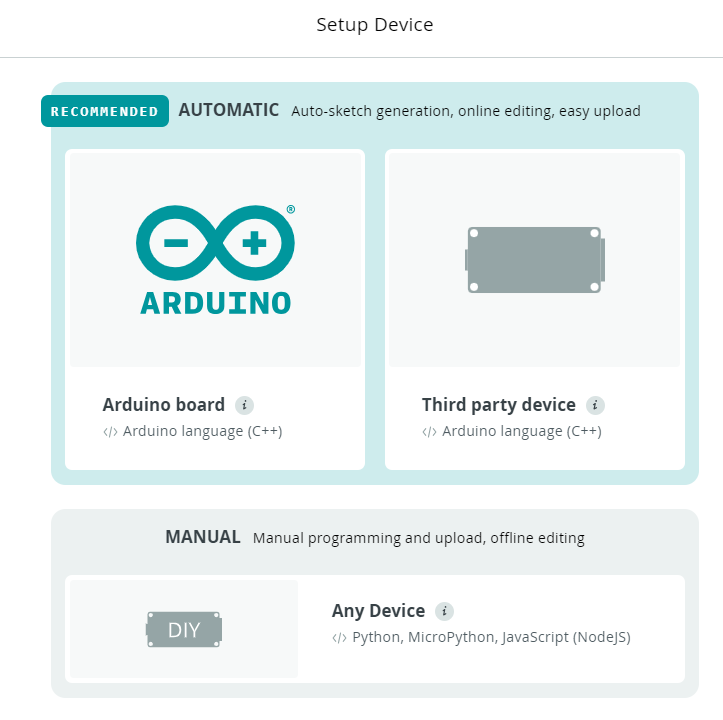
Now we’ll affiliate a tool to take action we have to click on choose Machine on the Related Machine part, and it’s essential to affiliate a brand new gadget, however first it’s essential to set up the drivers.
On this part you should have three choices, when you have an real Arduino board you’ll choose the Arduino Board choice and if you’re utilizing different improvement boards just like the ESP32 or ESP8266 you must choose the third get together board.
As soon as gadget setup is profitable you’ll be offered along with your Machine ID and Secret Key, save that as PDF and replica the Secret key to proceed additional.
As soon as that’s performed it’s essential to enter your Wi-Fi Credentials and the Secret Key and click on on Save. and you might be performed with this half.
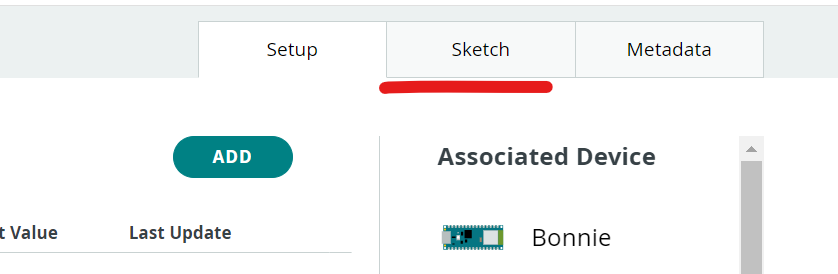 Now we have to click on on the sketch Tab. and we’ll write our code right here. The code may be very easy and the entire code is given on the backside of the web page within the Arduino Code Part.
Now we have to click on on the sketch Tab. and we’ll write our code right here. The code may be very easy and the entire code is given on the backside of the web page within the Arduino Code Part.
While you declare the variables within the setup part, the IoT cloud robotically creates the callback features for the variable and if any modifications is detected by the cloud the callback operate is named and the related motion will get executed.
Constructing a Dashboard
Now we have to create a dashboard for our challenge, when the dashboard is created you may management your utility with the dashboard out of your browser or your Android or IoS utility.
 While you click on on Construct Dashboard you’ll be offered with the above interface, and it’s essential to click on on the ADD button and it’s essential to choose the swap. Via which we’re going to be controlling the LED.
While you click on on Construct Dashboard you’ll be offered with the above interface, and it’s essential to click on on the ADD button and it’s essential to choose the swap. Via which we’re going to be controlling the LED.
Now it’s essential to assign a variable to the newly added widget. To take action click on on the Hyperlink Variable button and now we have to hyperlink the led variable with the swap. As soon as that’s performed will will add in a gauge and a proportion meter and fix the variable with it.
In case you have performed all the things accurately the code ought to compile high-quality and you’ll see the log within the serial monitor window.
Ultimate Code
/*
Sketch generated by the Arduino IoT Cloud Factor “Untitled”
https://create.arduino.cc/cloud/issues/f2395d6c-425a-44c5-9780-e415968881b1
Arduino IoT Cloud Variables description
The next variables are robotically generated and up to date when modifications are made to the Factor
float humidity;
float temperature;
CloudLight led;
Variables that are marked as READ/WRITE within the Cloud Factor will even have features
that are referred to as when their values are modified from the Dashboard.
These features are generated with the Factor and added on the finish of this sketch.
*/
#embrace “thingProperties.h”
#embrace “DHT.h”
#outline DHTPIN 5
#outline DHTTYPE DHT22
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
int interval=2000;
unsigned lengthy previousMillis=0;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial and look forward to port to open:
Serial.start(9600);
// This delay provides the prospect to attend for a Serial Monitor with out blocking if none is discovered
delay(1500);
dht.start();
// Outlined in thingProperties.h
initProperties();
// Hook up with Arduino IoT Cloud
ArduinoCloud.start(ArduinoIoTPreferredConnection);
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
/*
The next operate lets you acquire extra data
associated to the state of community and IoT Cloud connection and errors
the upper quantity the extra granular data you’ll get.
The default is 0 (solely errors).
Most is 4
*/
setDebugMessageLevel(2);
ArduinoCloud.printDebugInfo();
}
void loop() {
ArduinoCloud.replace();
// Your code right here
unsigned lengthy currentMillis = millis();
if ((unsigned lengthy)(currentMillis – previousMillis) >= interval) {
humidity = dht.readHumidity();
temperature = dht.readTemperature();
previousMillis = currentMillis;
}
}
/*
Since Led is READ_WRITE variable, onLedChange() is
executed each time a brand new worth is acquired from IoT Cloud.
*/
void onLedChange() {
(led == 1) ? digitalWrite(13,HIGH) :digitalWrite(13,LOW);
}
/*
Since Temperature is READ_WRITE variable, onTemperatureChange() is
executed each time a brand new worth is acquired from IoT Cloud.
*/
void onTemperatureChange() {
// Add your code right here to behave upon Temperature change
}
/*
Since Humidity is READ_WRITE variable, onHumidityChange() is
executed each time a brand new worth is acquired from IoT Cloud.
*/
void onHumidityChange() {
// Add your code right here to behave upon Humidity change
}
[ad_2]