![[INTERVIEW] From cells to strands: RPI researchers bioprint the constructing blocks of hair progress [INTERVIEW] From cells to strands: RPI researchers bioprint the constructing blocks of hair progress](https://bestnology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/3D-printed-hair-follicles-blog-image.webp)
[ad_1]
This yr noticed notable breakthroughs within the medical sector, together with a brand new software in 3D printing for hair follicle analysis by researchers at US-based Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI).
3D Printing Business interviewed Pankaj Karande, Affiliate Professor, Chemical and Organic Engineering at RPI to study extra about this novel research.
The analysis, additionally involving lead creator Carolina Catarino, and collaborative accomplice Grupo Boticario explores the potential for in vitro research to advance molecules selling hair progress and bettering transplantation success. This modern method holds promise for expediting complicated pores and skin graft growth, notably benefiting regenerative medication purposes corresponding to burn sufferer remedy.
“It’s tempting to assume that now we have now been in a position to develop an answer for hair restoration. Translation of our proof-of-concept research to demonstrating that we will type fully-grown hair in human pores and skin would require extra analysis and optimization. To not point out regulatory issues in translating this analysis to human sufferers. Our research have made essential contributions however there may be nonetheless quite a lot of work forward,” says Professor Karande.
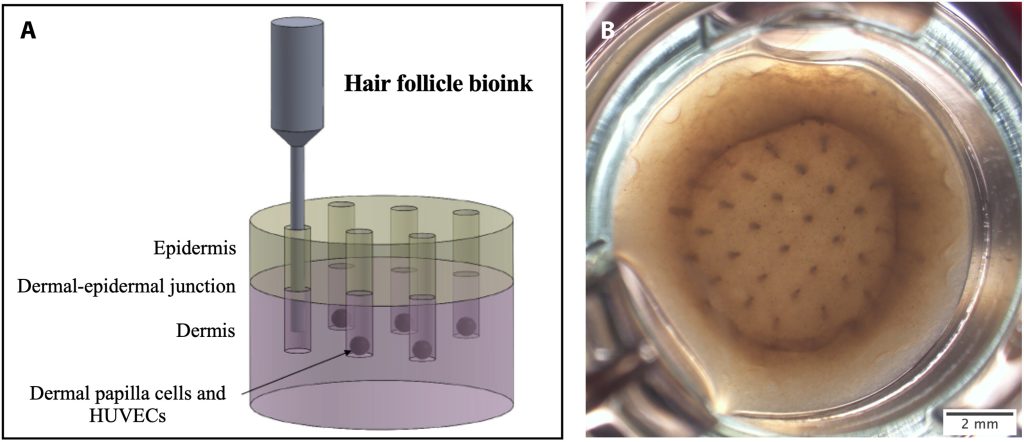
Bioprinting of useful hair follicles in pores and skin constructs
Professor Karande explains that to provide the bioprinted pores and skin pattern, the preliminary step includes designing bioinks composed of biomaterials corresponding to proteins and cells. Continuing with affected person consent, the group sourced these cells from discarded pores and skin samples both isolating them in-house or buying them commercially. The isolation course of takes roughly two weeks, after which the cells bear a cultivation and growth section within the laboratory lasting 1 to 4 weeks to extend their numbers. Subsequently, the cells are mixed with proteins and different biomaterials to formulate the bioinks.
The bioinks are then loaded into the bioprinting gear which may be very comparable in idea to the standard 3D printers. As an alternative of utilizing inks product of melted plastic, polymers, or resins, the group makes use of cartridges stuffed with organic materials. As soon as loaded, a pre-programmed algorithm guides the deposition of every materials, making a 3D tissue. “The method begins with the deposition of the bottommost layer (dermis), primarily composed of collagen I and dermal cells. After the dermis gels, the printing progresses to incorporate hair follicles and the exterior pores and skin layer (dermis). This complete printing course of for 12 samples (every about an inch in diameter) sometimes takes round 1 hour,” he mentioned.
Following printing, the samples bear incubation in a managed surroundings with common media adjustments, sustaining optimum temperature and CO2 ranges. This roughly 2-week incubation interval permits the tissue to mature to its remaining stage. Subsequently, the bioprinted pores and skin samples bear in vitro substance evaluations, signifying a serious development in numerous tissue engineering methods.
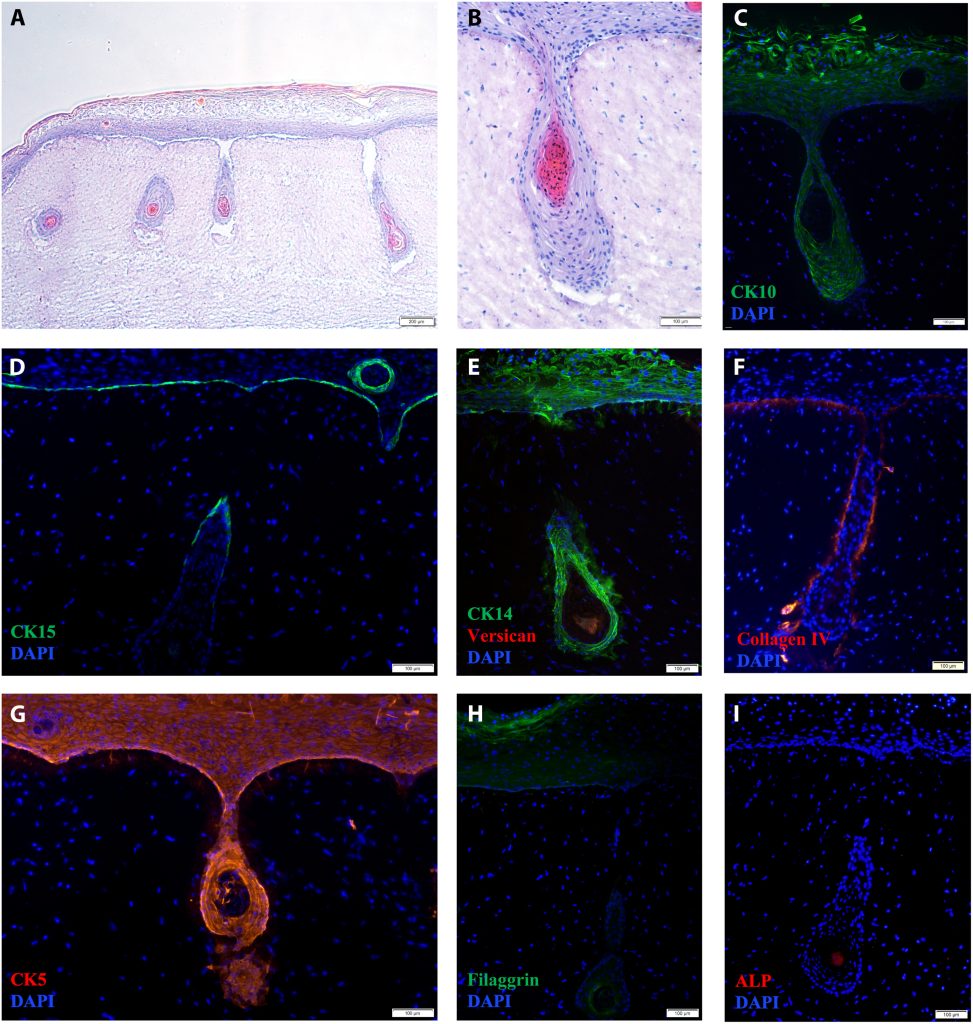
Revolutionizing hair follicle regeneration
He additional defined that reconstructing hair follicles utilizing human-derived cells is difficult as a result of lack of stem-cell-like traits exterior their pure surroundings. Cells battle to generate new follicles with out this context. Analysis means that culturing them in a three-dimensional surroundings partially restores their capability, probably forming new follicles or shafts. To deal with this problem, the group’s distinctive method makes use of bioprinting know-how to recreate the three-dimensional surroundings, facilitating the restoration of cell inductive capability in pores and skin mannequin reconstruction with hair follicles, in response to the Professor.
From a technical standpoint, the primary problem in realizing the undertaking concerned integrating numerous cell sorts into designated bioinks and aligning {hardware} and software program to construct useful human tissue. Coordinating these parts posed a big technical hurdle for the group, highlighting the complexity of advancing hair follicle regeneration.
“Once we discuss in vitro fashions for efficacy and toxicity testing of compounds, we don’t count on any aspect impact of getting hair follicle. The inclusion of such construction may improve our predictivity capability to know the impact of a compound for the reason that mannequin could be extra physiologically related and permit us to review different organic course of corresponding to hair progress,” he says. Concerning the potential use of those fashions for regenerative medication, there may be at all times the inherent threat of rejection by the physique corresponding to in any transplant. Sooner or later, the group plans to probably mix the know-how used to provide the fashions with using patient-derived cells utilizing iPSCs cells which might scale back the possibility of rejection.
Navigating bioprinting: customization and organic realities
Numerous bioprinting applied sciences, together with extrusion, inkjet, laser-assisted, and stereolithography, have been explored by researchers. Every know-how calls for customization in printing protocol, bioink composition, cross-linking mechanism, and curing. The mixture of bioinks, bioprinter, and printing program enabled the group to design a 3D mannequin inside related limitations, says the Professor.
“Nonetheless, although such know-how permits us to extend the complexity of what’s being created within the laboratory we nonetheless depend on biology to do a lot of the work. We will outline the hair density we want to print and even direct the expansion course; nevertheless, hair shade and fiber curvature are principally outlined by the DNA throughout the cells,” defined Professor Karande.
He additional defined that presently, the fashions developed are produced in a laboratory beneath managed situations of temperature, humidity, and with out direct daylight publicity. Shifting ahead within the growth of those fashions, environmental components corresponding to daylight publicity in addition to completely different humidity situations and software of gear will likely be evaluated to check the robustness of the mannequin.
Optimizing pores and skin mannequin complexity for future purposes
The introduced work is a proof of idea, demonstrating the effectivity of 3D bioprinting in enhancing the complexity of reconstructed pores and skin fashions. Whereas not but prepared for commercialization, the group is actively refining the printing protocol and bettering media composition for an prolonged tradition interval. Present bioprinters can produce a number of tissues or mini organoids of hair follicles inside an hour, and as know-how evolves, throughput is anticipated to extend. The main focus stays on advancing the approach and optimizing scalability for future purposes.
The Professor defined that the group’s goal is to optimize situations for sustained progress and maturation. They categorical curiosity in assessing the viability of the engineered tissue, notably the hair follicles, to develop hair shafts when grafted onto an animal mannequin. The following step includes transitioning to medical exams earlier than the know-how might be dropped at the market.
“We’re fascinated by exploring the potential of our mannequin for in vitro testing of various topical compounds and their efficiency or toxicity for varied medical and beauty purposes. For this case, as soon as these optimizations and in vitro validations have been carried out, the mannequin could possibly be commercialized. Keep tuned for forthcoming updates as we intention to share our progress and findings via publications within the close to future,” concluded Professor Karande.
Learn all of the 3D Printing Business protection from Formnext 2023.
What does the way forward for 3D printing for the following ten years maintain?
What engineering challenges will have to be tackled within the additive manufacturing sector within the coming decade?
To remain updated with the newest 3D printing information, don’t overlook to subscribe to the 3D Printing Business publication or observe us on Twitter, or like our web page on Fb.
Whilst you’re right here, why not subscribe to our Youtube channel? That includes dialogue, debriefs, video shorts, and webinar replays.
Are you on the lookout for a job within the additive manufacturing business? Go to 3D Printing Jobs for a collection of roles within the business.
Featured picture exhibits from left to proper: Pankaj Karande and Carolina Catarino. Picture by way of RPI.
[ad_2]