
[ad_1]

Calculating a year-to-date whole is a standard activity when monitoring earnings, and thankfully, it’s simple so as to add to a Energy BI report. It’s a kind of working whole — a regularly adjusting whole that provides and subtracts values as they happen for a particular 12 months. Whenever you want such totals, don’t scour the web for the Knowledge Evaluation Expressions code as a result of fast measures can be found for each kinds of working totals.
On this tutorial, I’ll present you how you can add a easy working whole and a YTD whole to a easy dataset in Energy BI. I’m utilizing Microsoft Energy BI on a Home windows 11 64-bit system with a easy .pbix demonstration file you may obtain. If you wish to begin from scratch, you may obtain the .xlsx file that accommodates the info, which you’ll then import into Energy BI.
Leap to:
Learn how to put together the info set in Energy BI
For demonstration functions, we’ll work with a easy dataset that accommodates a column of distinctive dates. You may work with your personal information should you favor, however the demonstration dates are distinctive, which is able to make a distinction. When working with your personal information, you most likely don’t want so as to add the Date desk; probably, it already exists inside your Energy BI file.
SEE: Right here’s what it’s good to learn about Microsoft Energy Platform.
Determine A exhibits the connection between the information desk, Gross sales, and a customized date desk, Date. Particularly, there’s a one-to-one relationship between Gross sales Date (Gross sales desk) and Date (Date desk).
Determine A

Determine B exhibits the operate in Itemizing A used to create the date desk.
Determine B
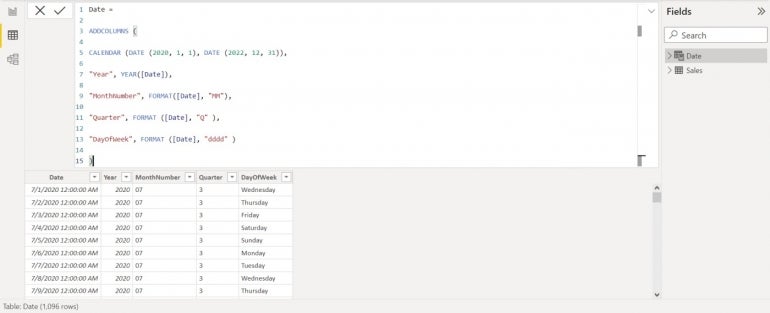
Itemizing A
Date =
ADDCOLUMNS (
CALENDAR (DATE (2020, 1, 1), DATE (2022, 12, 31)),
"12 months", YEAR([Date]),
"MonthNumber", FORMAT([Date], "MM"),
"Quarter", FORMAT ([Date], "Q" ),
"DayOfWeek", FORMAT ([Date], "dddd" )
)Crucial a part of the date desk is the YEAR operate, which returns the years 2021 via 2022 as a result of the information desk accommodates dates for the years 2021 and 2022. It isn’t mandatory to incorporate 2020, as we did utilizing the CALENDAR operate, however it doesn’t harm to take action. Nonetheless, you could accommodate the prevailing 12 months values in your information for this to work appropriately when creating your personal date desk.
If you happen to’re not accustomed to the date desk, you may wish to learn Learn how to know if the Auto date desk is enough when utilizing Energy BI or Learn how to create a date desk in Microsoft Energy BI.
With the tables and relationship in place, you’re prepared to begin analyzing the info.
SEE: Learn to create a dashboard in Energy BI.
Learn how to calculate a easy working whole in Energy BI
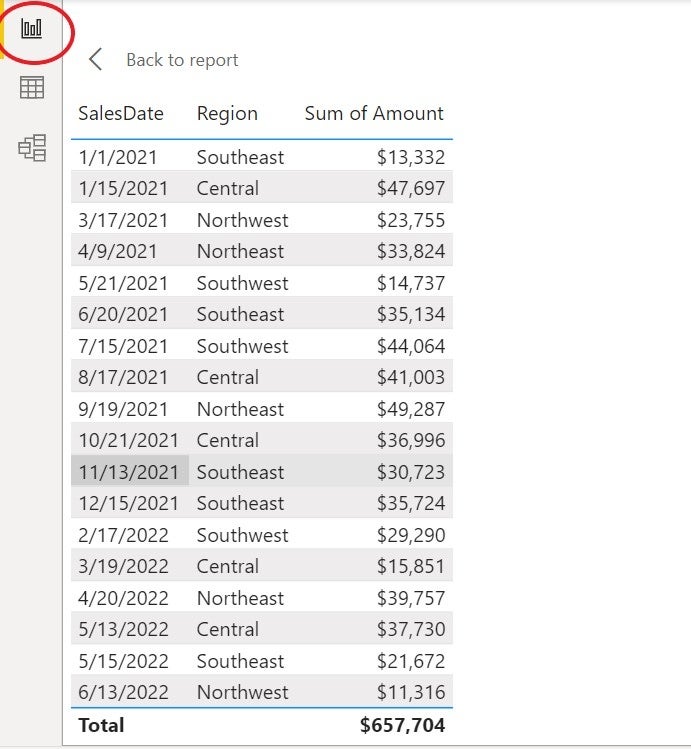
Now, let’s suppose you’re requested so as to add a working whole to the straightforward desk visualization proven in Determine C. You may attempt to create the mandatory DAX code your self, however that’s not mandatory as a result of Energy BI has a fast measure that may calculate a working whole.
Determine C
So as to add a working whole measure to the dataset, do the next in Report view:
1. Click on the Gross sales desk within the Knowledge pane so as to add the measure to this desk.
2. Click on the Desk Instruments contextual tab.
3. Within the Calculations group, click on Fast Measure.
4. Within the ensuing dialog, select Working Complete from the Calculation dropdown.
5. Increase the Gross sales desk (to the precise) within the Knowledge pane, if mandatory, and add the Quantity area to the Base Worth bucket.
6. Add the SalesDate area to the Discipline bucket (Determine D).
Determine D

7. Click on Add.
Energy BI provides the fast measure to the Gross sales desk (Determine E). Add the fast measure to the desk visualization by checking it within the Knowledge pane. To see the DAX code, click on the components bar’s dropdown arrow. As you may see, the brand new column provides the present worth to the earlier whole for each file.
Determine E

SEE: Uncover how you can add a calculated column in Microsoft Energy BI.
Discover the underlying DAX code
The fast measure is way simpler to implement than the code, so let’s take a minute to see how the underlying DAX code works:
- The primary line is the default title, which you’ll change by right-clicking the measure within the Knowledge pane and selecting Rename.
- The SUM operate evaluates the Quantity area within the Gross sales desk, which you specified when creating the fast measure.
- The FILTER operate is perhaps a little bit of a shock, however it’s the ISONORAFTER operate that does the heavy lifting by specifying the present worth and all these above.
There’s definitely quite a bit occurring. That’s why I like to recommend checking fast measures earlier than attempting to jot down DAX code your self.
Now, let’s see what Energy BI has to supply in the way in which of returning a YTD column.
SEE: Deal with DAX fundamentals in Microsoft Energy BI.
Learn how to calculate a YTD whole in Energy BI
A YTD whole evaluates values with the identical 12 months worth. We’ll be utilizing one other fast measure, which is able to reset to 0 and begin over when encountering a brand new 12 months worth. It’s just like a working whole, however it’s a collection of working totals fairly than one steady working whole. Fortuitously, it’s simply as simple to create because the working whole:
1. Click on the Gross sales desk within the Knowledge pane so as to add the measure to this desk.
2. Click on the Desk Instruments contextual tab.
3. Within the Calculations group, click on Fast Measure.
4. Within the ensuing dialog, select 12 months-To-Date Complete from the Calculation dropdown.
5. Increase the Gross sales desk (to the precise), and add the Quantity area to the Base Worth bucket.
6. Increase the Date desk, and add Date to the Discipline bucket (Determine F).
Determine F

7. Click on Add.
Add the brand new measure, Quantity YTD, to the visualization (Determine G). Discover that the returned values are the identical as these within the working totals column till the date 2/17/22. That’s as a result of the 12 months modified from 2021 to 2022.
Determine G

Apparently, the DAX code is way less complicated this time:
- The primary line is the measure’s default title.
- The second line makes use of the TOTALYTD operate to calculate the Quantity values by the 12 months.
SEE: Learn to add fast measures for advanced calculations in Microsoft Energy BI Desktop.
You might need seen that the straightforward working whole measure pulls quantities and dates from the Gross sales desk and that the YTD working whole pulls quantities from the Gross sales desk and dates from the Date desk. That’s as a result of there aren’t any 12 months values within the information desk, Gross sales. That’s the place the connection mentioned firstly of this text comes into play.
The reality is, the straightforward working whole might additionally use the Date column from the Knowledge desk. In truth, you probably have duplicate dates, you need to accomplish that if you need a easy working whole.
If in case you have duplicate dates within the information desk and you utilize the SalesDate column within the information desk, the measure will begin over on the duplicate date, returning a working whole inside a working whole. Which will or might not be what you need, so it’s necessary that you simply perceive how the connection between the 2 tables works when including a working whole.
I like to recommend you all the time examine what fast measures can be found earlier than you attempt to write DAX code your self. You is perhaps shocked at how a lot they will do.
[ad_2]