[ad_1]
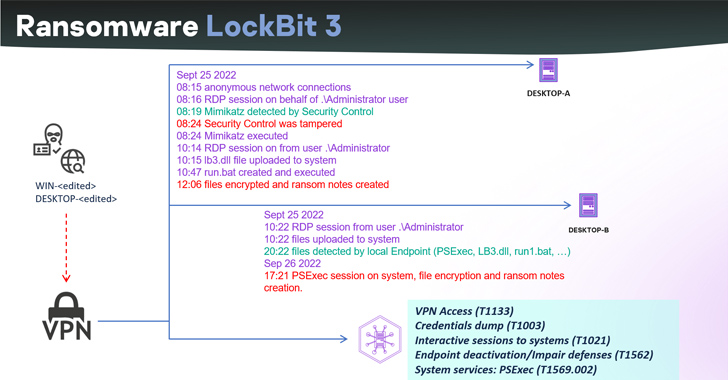
The leak of the LockBit 3.0 ransomware builder final 12 months has led to risk actors abusing the instrument to spawn new variants.
Russian cybersecurity firm Kaspersky mentioned it detected a ransomware intrusion that deployed a model of LockBit however with a markedly completely different ransom demand process.
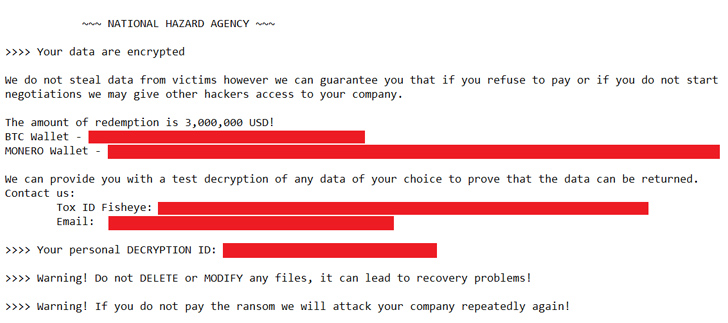
“The attacker behind this incident determined to make use of a distinct ransom notice with a headline associated to a beforehand unknown group, referred to as NATIONAL HAZARD AGENCY,” safety researchers Eduardo Ovalle and Francesco Figurelli mentioned.
The revamped ransom notice straight specified the quantity to be paid to acquire the decryption keys, and directed communications to a Tox service and electronic mail, in contrast to the LockBit group, which does not point out the quantity and makes use of its personal communication and negotiation platform.
NATIONAL HAZARD AGENCY is much from the one cybercrime gang to make use of the leaked LockBit 3.0 builder. Among the different risk actors recognized to leverage it embrace Bl00dy and Buhti.
Kaspersky famous it detected a complete of 396 distinct LockBit samples in its telemetry, of which 312 artifacts had been created utilizing the leaked builders. As many as 77 samples make no reference to “LockBit” within the ransom notice.
“Lots of the detected parameters correspond to the default configuration of the builder, just some comprise minor adjustments,” the researchers mentioned. “This means the samples had been probably developed for pressing wants or presumably by lazy actors.”
The disclosure comes as Netenrich delved right into a ransomware pressure referred to as ADHUBLLKA that has rebranded a number of instances since 2019 (BIT, LOLKEK, OBZ, U2K, and TZW), whereas focusing on people and small companies in trade for meager payouts within the vary of $800 to $1,600 from every sufferer.

Though every of those iterations include slight modifications to encryption schemes, ransom notes, and communication strategies, a better inspection has tied all of them again to ADHUBLLKA owing to supply code and infrastructure similarities.
“When a ransomware is profitable out within the wild, it’s common to see cybercriminals use the identical ransomware samples — barely tweaking their codebase — to pilot different initiatives,” safety researcher Rakesh Krishnan mentioned.
“For instance, they could change the encryption scheme, ransom notes, or command-and-control (C2) communication channels after which rebrand themselves as a ‘new’ ransomware.”
Ransomware stays an actively evolving ecosystem, witnessing frequent shifts in ways and focusing on to more and more deal with Linux environments utilizing households resembling Trigona, Monti, and Akira, the latter of which shares hyperlinks to Conti-affiliated risk actors.
Akira has additionally been linked to assaults weaponizing Cisco VPN merchandise as an assault vector to realize unauthorized entry to enterprise networks. Cisco has since acknowledged that the risk actors are focusing on Cisco VPNs that aren’t configured for multi-factor authentication.
“The attackers usually deal with the absence of or recognized vulnerabilities in multi-factor authentication (MFA) and recognized vulnerabilities in VPN software program,” the networking tools main mentioned.
“As soon as the attackers have obtained a foothold right into a goal community, they attempt to extract credentials by way of LSASS (Native Safety Authority Subsystem Service) dumps to facilitate additional motion throughout the community and elevate privileges if wanted.”
The event additionally comes amid a report surge in ransomware assaults, with the Cl0p ransomware group having breached 1,000 recognized organizations by exploiting flaws in MOVEit Switch app to realize preliminary entry and encrypt focused networks.

U.S.-based entities account for 83.9% of the company victims, adopted by Germany (3.6%), Canada (2.6%), and the U.Okay. (2.1%). Greater than 60 million people are mentioned to have been impacted by the mass-exploitation marketing campaign that started in Could 2023.
Nonetheless, the blast radius of the provide chain ransomware assault is more likely to be a lot greater. Estimates present that the risk actors are anticipated to web illicit earnings within the vary of $75 million to $100 million from their endeavors.
“Whereas the MOVEit marketing campaign could find yourself impacting over 1,000 firms straight, and an order of magnitude extra not directly, a really very small proportion of victims bothered making an attempt to barter, not to mention contemplated paying,” Coveware mentioned.
“People who did pay, paid considerably greater than prior CloP campaigns, and several other instances greater than the worldwide Common Ransom Quantity of $740,144 (+126% from Q1 2023).”
What’s extra, based on Sophos 2023 Lively Adversary Report, the median dwell time for ransomware incidents dropped from 9 days in 2022 to 5 days within the first half of 2023, indicating that “ransomware gangs are shifting sooner than ever.”
In distinction, the median dwell time for non-ransomware incidents elevated from 11 to 13 days. The utmost dwell time noticed through the time interval was 112 days.
“In 81% of ransomware assaults, the ultimate payload was launched exterior of conventional working hours, and for those who had been deployed throughout enterprise hours, solely 5 occurred on a weekday,” the cybersecurity firm mentioned. “Almost half (43%) of ransomware assaults had been detected on both Friday or Saturday.”
[ad_2]