[ad_1]
Folks have been captivated by the thought of helicopter flight for hundreds of years. A craft that may permit one not solely to fly by the air like a hawk, but in addition to hover, stationary, like a bumblebee. Italian multipotentialite (or polymath, in case you want) Leonardo da Vinci drew his design for the “aerial screw” means again within the 1480s. The idea itself can really be traced again even additional to the Chinese language flying high, circa 1100.
Chinese language Flying High (credit score: Encyclopedia Brittanica); DaVinci’s Aerial Screw (CC); Mars Ingenuity (credit score: NASA/JPL)
It might take virtually 5 centuries earlier than flight in a craft with horizontal rotors would turn out to be a actuality, and because of their means to take off and land vertically, in addition to hover in place, helicopters proceed to be the go-to selection for a lot of film-makers, information stations, search-and-rescue missions, and even navy forces for sure forms of operations. It’s even doable for the likes of you and I to take a spin in a helicopter. Victoria Falls in Zimbabwe, the Grand Canyon in Arizona, the Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers in New Zealand, Maui and Molokai in Hawaii – a few of the most spectacular views of a few of the most unbelievable sights on the earth can solely be seen by renting an hour or two in a helicopter, and by all accounts, each one in every of these journeys is really spectacular.
However at the moment I wish to speak about a special helicopter journey. One which no human has ever taken, however is maybe extra spectacular than every other in our lifetime. I’m speaking in regards to the first helicopter flight on a planet aside from our personal. I’m speaking, in fact, in regards to the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter.
Engineers modifying Ingenuity flight mannequin inside NASA JPL’s Area Simulator. (Picture: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Ingenuity was constructed as a proof of idea piece. Whereas so lots of NASA’s rovers and deep house explorers are categorized as Class B missions, utilizing ruggedized {hardware} and software program designed for the trials of house, this Mars helicopter was categorized as a know-how demo. This allowed the workforce a bit of extra flexibility and freedom. This meant that they weren’t relegated to particular, examined and verified elements for the construct. This turned out to be supremely vital.
One of many greatest points going through the engineers was Mars’s lack of ambiance. The Martian ambiance is just about 1% the density of that on Earth. That signifies that carry could be very troublesome to attain and keep, so the helicopter would have to be as mild as doable. For instance, in case you’ve ever gone up into the mountains to fly a drone or UAV, you’ve little doubt seen that it has a bit extra hassle getting up into the air. That’s as a result of the ambiance is thinner the upper we climb. A helicopter on Earth can attain a most altitude of about 25,000 toes (7620 meters) earlier than the air is simply too skinny to help the craft on its blades. The ambiance on Mars, nevertheless, is the equal of making an attempt to fly at 80,000 toes (24384 meters) on Earth. This meant that the craft needed to be as mild as doable. Theoretical calculations dictated that the craft would weigh not more than 4 lbs, or simply underneath 2 kg. The usual pc used for working most spacecrafts is the RAD750 from BAE System, which weighs a couple of pound. Utilizing one fourth of the craft’s whole weight allowance wasn’t possible, and with out the constraints of a Class B mission, the workforce was free to search for options. They wound up utilizing a Qualcomm Snapdragon 801 processor, which was lighter, extra highly effective, and much inexpensive than the RAD750.
Off-the-shelf elements turned an vital a part of Ingenuity’s construct. Rechargeable batteries, avionics, cameras and sensors may all be sourced from corporations like SparkFun, and used not just for preliminary prototyping, however for the precise mission itself. In an interview with IEEE Spectrum earlier than Ingenuity even had its toes on Martian soil, JPL engineer Tim Canham talked in regards to the significance of with the ability to use commercially obtainable elements from begin to end, and calls out SparkFun and the laser altimeter they used for takeoff and touchdown. (Excellent news – you possibly can nonetheless get one for the following mission, no matter how removed from dwelling it’s!)
A TIMELINE OVERVIEW
The Mars Perseverance positioned Ingenuity gently down onto the floor of Mars on April 3, 2021. The primary take a look at was merely to see if Ingenuity would survive the evening, and nonetheless be capable to talk within the morning. On April 4, success of step one was confirmed. 4 days later, the rotors had been despatched a spin take a look at command, which it executed completely. Then, per week and a half later, on April nineteenth, 2021, the Mars Ingenuity Helicopter efficiently accomplished its first flight, the primary powered, managed flight of any craft, on a planet aside from Earth. It was an especially thrilling day, and whereas I don’t know if I can communicate for SparkFun as an entire, I do know that personally my major curiosity was targeted on seeing the helicopter execute an ideal touchdown. In any case, I had been bragging about SparkFun elements on Mars, and the way the Lidar Lite v3 would help within the craft’s touchdown. I actually didn’t need any concern to look in any option to have been as a result of an element from SparkFun.
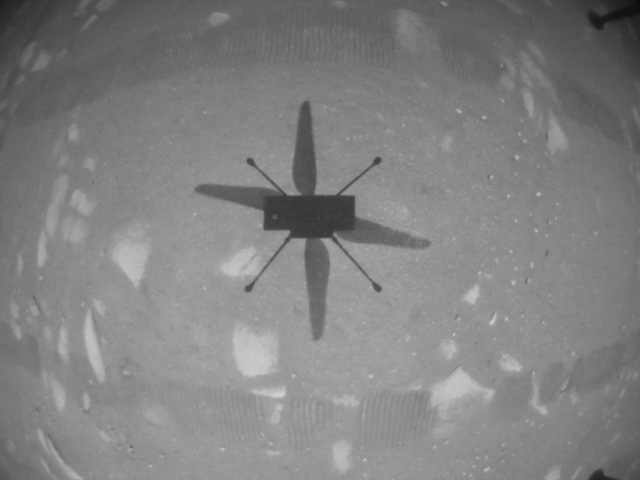
Me and my shadow. Ingenuity sends again a picture of its personal shadow on the Mars panorama from its maiden voyage. (Picture: NASA)
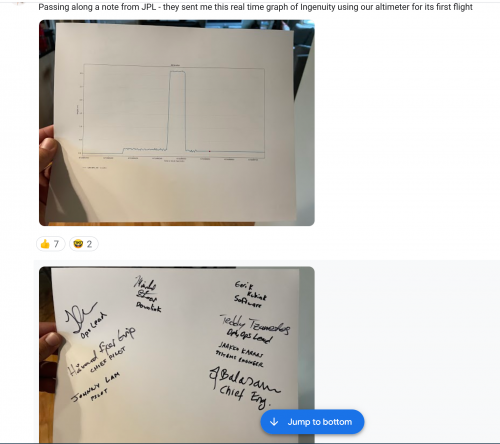
Fortunately, the lift-off, flight, and touchdown all went off with no hitch. By NASA’s personal account, this meant that the whole mission of Ingenuity had been a hit! They’ve proved that managed, powered flight on Mars was doable. An incredible feat by a gaggle of extremely sensible and funky engineers at NASA JPL. Oh, and in case you’re questioning whether or not or not they’re really cool – after that first flight, the engineers despatched Glenn, our CEO, a signed copy of the real-time altimeter studying from that first flight. Coolness confirmed!
After its first flight, the Ingenuity Workforce at NASA despatched Glenn, our CEO, an actual time graph of the altimeter studying, signed by everybody there!
Ingenuity began with the intent of creating 5 complete flights, with solely the primary three flights having been pre-planned, all of which might be accomplished inside thirty days. The primary three makes an attempt would take off and land in the identical spot, though for flight quantity three, they hoped to have the ability to get the helicopter to carry off, journey roughly 50 meters, then return again and land at its unique spot. The primary three flights had been accomplished inside per week, and for all of them, Ingenuity carried out fantastically. For the following two flights, Ingenuity would perform a little extra touring. On April twentieth, the primary try of flight 4 failed when the onboard software program didn’t transition to flight mode. Heads had been scratched, espresso was consumed, updates had been despatched, and by the following day, Ingenuity accomplished its fourth flight, this time touring out 130 meters for a bit of scouting enterprise of what could be referred to as Airfield B, taking each coloration and black-and-white photos, then returning to settle again down at its start line. As well as, the Perseverance rover recorded each video and audio of the flight, making this the primary interplanetary automobile to have its sound recorded outdoors of Earth. Then, on Might seventh, 2021, Ingenuity made its last flight of the preliminary 5, and touched down at its new level, Airfield B, some 130 meters from its origin at Airfield A.
We now have robots sending us photos of different robots from completely different planets! Ingenuity, as photographed by Perseverance.(Picture: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS)
The little helicopter nonetheless had energy, and because the preliminary outcomes and returns had been so good, they determined to proceed ahead. In any case, any extra data gained at this level was pure bonus. So on Might twenty third, Ingenuity ventured previous its unique 5-flight mission, and accomplished flight 6. This flight lifted as much as ten meters, and at 4 km, its quickest airspeed but, and landed simply over 202 meters away, at touchdown Airfield C. There have been some in-flight points, and the craft wound up turning off the navigation digital camera and flying solely on IMU. This was the primary time that Ingenuity needed to land at a web site it had not beforehand surveyed, however had solely been surveyed by MRO satellite tv for pc. Harrowing because it was, the sixth flight was a hit.
After that, the little copter that might simply saved on going. It recorded its tenth flight on July twenty fourth, touring 240 meters to what could be its seventh touchdown web site, Airfield G, and taking surveying pictures alongside the best way. At this level, the helicopter modified to a surveying mission, to help the work of the Perseverance rover. It might exit on scouting journeys to assist dictate the perfect journey path for the rover because it made its means round Jezero Crater. A few of its highlights embody:
Flight 12: Longest period. On August sixteenth, 2021, Ingenuity spent 169.5 seconds in flight, the longest of its missions.
Flight 25: Longest distance. On April eighth, 2022, virtually a full Earth 12 months after Ingenuity’s first flight on Mars, the automobile flew for 708.91 meters to Airfield Q, its seventeenth touchdown space.
Flight 61: Highest altitude. On October fifth, 2023, in a take a look at of Ingenuity’s flight envelope, the craft lifted itself to an altitude of 24 meters, for a flight that lasted over two minutes.
Flight 62: Quickest land pace. October twelfth, 2023. “Hey, keep in mind final week once we noticed how excessive we may go?”
“Yeah.”
“Wanna see how briskly we will go?”
“Positive!”
Ingenuity reaches a pace of 10 m/s, or 22mph, for a flight of simply over two minutes.
Flight 72: Remaining flight. On January 18, 2024, after a brief flight for a methods verify and verification, pictures from Ingenuity’s horizon and navigation cameras confirmed clear injury to the ideas of its rotors. It was apparent that the craft would not be able to secure flight, and at that time NASA had no different however to floor the helicopter. Every week later, on January twenty fifth, 2024, NASA administrator Invoice Nelson introduced that after three years on the pink planet, Ingenuity’s mission had come to an finish.
Ingenuity sees it shadow, and apparently on Mars, which means no extra aerial missions. (Picture: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
LOOKING AHEAD
Whereas future essential NASA missions, i.e. these involving human life, will proceed to make use of space-rated {hardware}, the teachings realized from Ingenuity’s large successes will little doubt permit for extra freedom when designing know-how demonstration missions sooner or later. In response to NASA’s Theodore Tzanetos, Ingenuity Workforce Lead, “This can be a large victory for engineers.” Utilizing off-the-shelf elements will permit for tech demo missions to be inexpensive, lighter, and higher-performing. I personally am very excited for NASA’s upcoming Dragonfly mission. I additionally know that when, sooner or later sooner or later, I see pictures being despatched from a helicopter on Titan, or our moon, or every other celestial physique, I’ll at all times suppose again to when NASA put elements from SparkFun on Mars for the very first powered flight from anyplace aside from Earth.
Artist’s impression of Dragonfly, the NASA aerial automobile that will probably be heading to Titan in 2028. (Picture:NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Steve Gribben)
WANT MORE INFORMATION?
If you happen to, like me, can’t get sufficient information on stuff you discover fascinating, listed below are just a few hyperlinks to maintain you studying.
[ad_2]