
[ad_1]

The P2PInfect botnet worm goes by way of a interval of extremely elevated exercise volumes beginning in late August after which selecting up once more in September 2023.
P2PInfect was first documented by Unit 42 in July 2023 as a peer-to-peer malware that breaches Redis cases utilizing a distant code execution flaw on internet-exposed Home windows and Linux programs.
Cado Safety researchers who’ve been following the botnet since late July 2023, report right this moment seeing world exercise, with most breaches impacting programs in China, the US, Germany, Singapore, Hong Kong, the UK, and Japan.
Moreover, Cado says the newest P2PInfect samples function additions and enhancements that make it extra able to spreading to targets and showcase the continual improvement of the malware.
Steep rise in exercise
Cado sees P2PInfect botnet exercise, indicating that the malware has entered a brand new interval of code stability that enables it to ramp up its operation.
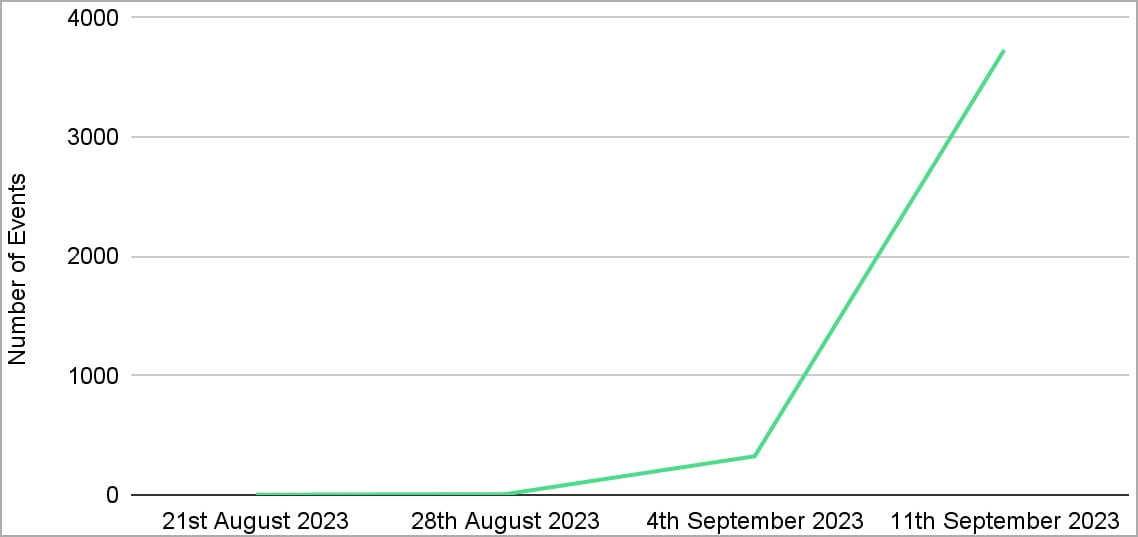
The researchers report observing a gradual improve within the variety of preliminary entry makes an attempt carried out by P2PInfect on their honeypots, resulting in 4,064 occasions from a single sensor as of August 24, 2023.
By September 3, 2023, preliminary entry occasions had tripled however remained comparatively low.
Then, within the week between the twelfth and nineteenth of September 2023, a surge in P2PInfect exercise occurred, with Cado recording 3,619 entry makes an attempt throughout this era alone, which is a 600x rise.
“This improve in P2Pinfect visitors has coincided with a rising variety of variants seen within the wild, suggesting that the malware’s builders are working at a particularly excessive improvement cadence,” explains Cado.
New P2PInfect options
Alongside the elevated exercise, Cado noticed new samples that make P2PInfect a stealthier and extra formidable menace.
First, the malware’s authors have added a cron-based persistence mechanism that replaces the earlier ‘bash_logout’ methodology, triggering the principle payload each half-hour.

Moreover, P2Pinfect now makes use of a (secondary) bash payload to speak with the first payload by way of an area server socket, and if the principle course of stops or is deleted, it retrieves a duplicate from a peer and restarts it.
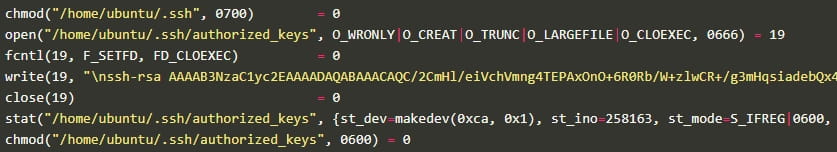
The malware now additionally makes use of an SSH key to overwrite any SSH authorized_keys on the breached endpoint to stop professional customers from logging in by way of SSH.
If the malware has root entry it’s going to carry out a password change for another customers on the system utilizing an mechanically generated 10-character password to lock them out.
Lastly, P2PInfect now makes use of a C struct configuration for its consumer that’s up to date dynamically in reminiscence, whereas beforehand, it did not have a configuration file.
Unclear objectives
Cado studies that the P2PInfect variants it noticed just lately tried to fetch a miner payload however didn’t see precise cryptomining exercise on compromised gadgets. Subsequently, it is unclear if the malware operators are nonetheless experimenting with the ultimate step of the assault.
The botnet’s operators could also be enhancing the miner part or in search of patrons of subscriptions to P2PInfect, so that they use the miner as a dummy for demonstration.
Given the present botnet’s measurement, unfold, self-updating options, and quick growth this month, P2PInfect is a considerable menace to regulate.
[ad_2]