[ad_1]
Generative AI is in every single place. With the flexibility to provide textual content, photographs, video, and extra, it’s thought of probably the most impactful rising know-how of the following three to 5 years by 77% of executives. Although generative AI has been researched for the reason that Sixties, its capabilities have expanded in recent times attributable to unprecedented quantities of coaching knowledge and the emergence of basis fashions in 2021. These elements made applied sciences like ChatGPT and DALL-E potential and ushered within the widespread adoption of generative AI.
Nonetheless, its fast affect and progress additionally yields a myriad of moral issues, says Surbhi Gupta, a GPT and AI engineer at Toptal who has labored on cutting-edge pure language processing (NLP) initiatives starting from chatbots and marketing-related content material technology instruments to code interpreters. Gupta has witnessed challenges like hallucinations, bias, and misalignment firsthand. For instance, she observed that one generative AI chatbot meant to establish customers’ model goal struggled to ask customized questions (relying on normal business traits as a substitute) and failed to answer surprising, high-stakes conditions. “For a cosmetics enterprise, it could ask questions concerning the significance of pure components even when the user-defined distinctive promoting level was utilizing customized formulation for various pores and skin sorts. And after we examined edge circumstances akin to prompting the chatbot with self-harming ideas or a biased model concept, it generally moved on to the following query with out reacting to or dealing with the issue.”
Certainly, previously 12 months alone, generative AI has unfold incorrect monetary knowledge, hallucinated pretend court docket circumstances, produced biased photographs, and raised a slew of copyright issues. Although Microsoft, Google, and the EU have put forth finest practices for the event of accountable AI, the consultants we spoke to say the ever-growing wave of latest generative AI tech necessitates further pointers attributable to its unchecked progress and affect.
Why Generative AI Ethics Are Necessary—and Pressing
AI ethics and laws have been debated amongst lawmakers, governments, and technologists across the globe for years. However current generative AI will increase the urgency of such mandates and heightens dangers, whereas intensifying current AI issues round misinformation and biased coaching knowledge. It additionally introduces new challenges, akin to guaranteeing authenticity, transparency, and clear knowledge possession pointers, says Toptal AI knowledgeable Heiko Hotz. With greater than 20 years of expertise within the know-how sector, Hotz at the moment consults for international firms on generative AI subjects as a senior options architect for AI and machine studying at AWS.
|
Misinformation |
The principle threat was blanket misinformation (e.g., on social media). Clever content material manipulation by packages like Photoshop could possibly be simply detected by provenance or digital forensics, says Hotz.
|
Generative AI can speed up misinformation because of the low price of making pretend but life like textual content, photographs, and audio. The power to create customized content material primarily based on a person’s knowledge opens new doorways for manipulation (e.g., AI voice-cloning scams) and difficulties in detecting fakes persist.
|
|
Bias |
Bias has all the time been a giant concern for AI algorithms because it perpetuates current inequalities in main social programs akin to healthcare and recruiting. The Algorithmic Accountability Act was launched within the US in 2019, reflecting the issue of elevated discrimination.
|
Generative AI coaching knowledge units amplify biases on an unprecedented scale. “Fashions decide up on deeply ingrained societal bias in large unstructured knowledge (e.g., textual content corpora), making it laborious to examine their supply,” Hotz says. He additionally factors to the chance of suggestions loops from biased generative mannequin outputs creating new coaching knowledge (e.g., when new fashions are skilled on AI-written articles). |
Specifically, the potential incapability to find out whether or not one thing is AI- or human-generated has far-reaching penalties. With deepfake movies, life like AI artwork, and conversational chatbots that may mimic empathy, humor, and different emotional responses, generative AI deception is a prime concern, Hotz asserts.
Additionally pertinent is the query of information possession—and the corresponding legalities round mental property and knowledge privateness. Giant coaching knowledge units make it tough to achieve consent from, attribute, or credit score the unique sources, and superior personalization talents mimicking the work of particular musicians or artists create new copyright issues. As well as, analysis has proven that LLMs can reveal delicate or private info from their coaching knowledge, and an estimated 15% of staff are already placing enterprise knowledge in danger by frequently inputting firm info into ChatGPT.
5 Pillars of Constructing Accountable Generative AI
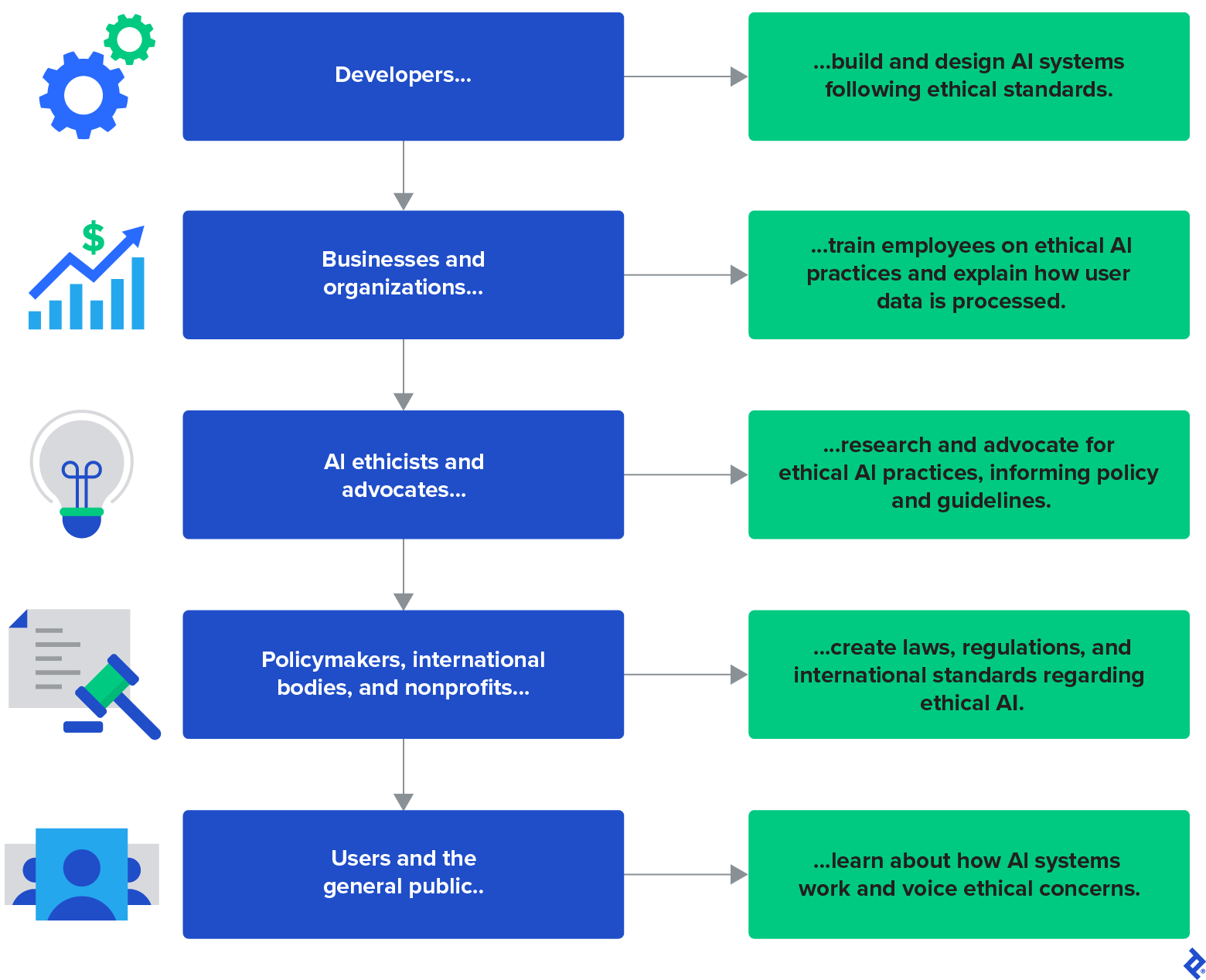
To fight these wide-reaching dangers, pointers for growing accountable generative AI needs to be quickly outlined and carried out, says Toptal developer Ismail Karchi. He has labored on quite a lot of AI and knowledge science initiatives—together with programs for Jumia Group impacting hundreds of thousands of customers. “Moral generative AI is a shared duty that entails stakeholders in any respect ranges. Everybody has a job to play in guaranteeing that AI is utilized in a approach that respects human rights, promotes equity, and advantages society as an entire,” Karchi says. However he notes that builders are particularly pertinent in creating moral AI programs. They select these programs’ knowledge, design their construction, and interpret their outputs, and their actions can have massive ripple results and have an effect on society at massive. Moral engineering practices are foundational to the multidisciplinary and collaborative duty to construct moral generative AI.
To attain accountable generative AI, Karchi recommends embedding ethics into the observe of engineering on each instructional and organizational ranges: “Very like medical professionals who’re guided by a code of ethics from the very begin of their schooling, the coaching of engineers must also incorporate basic ideas of ethics.”
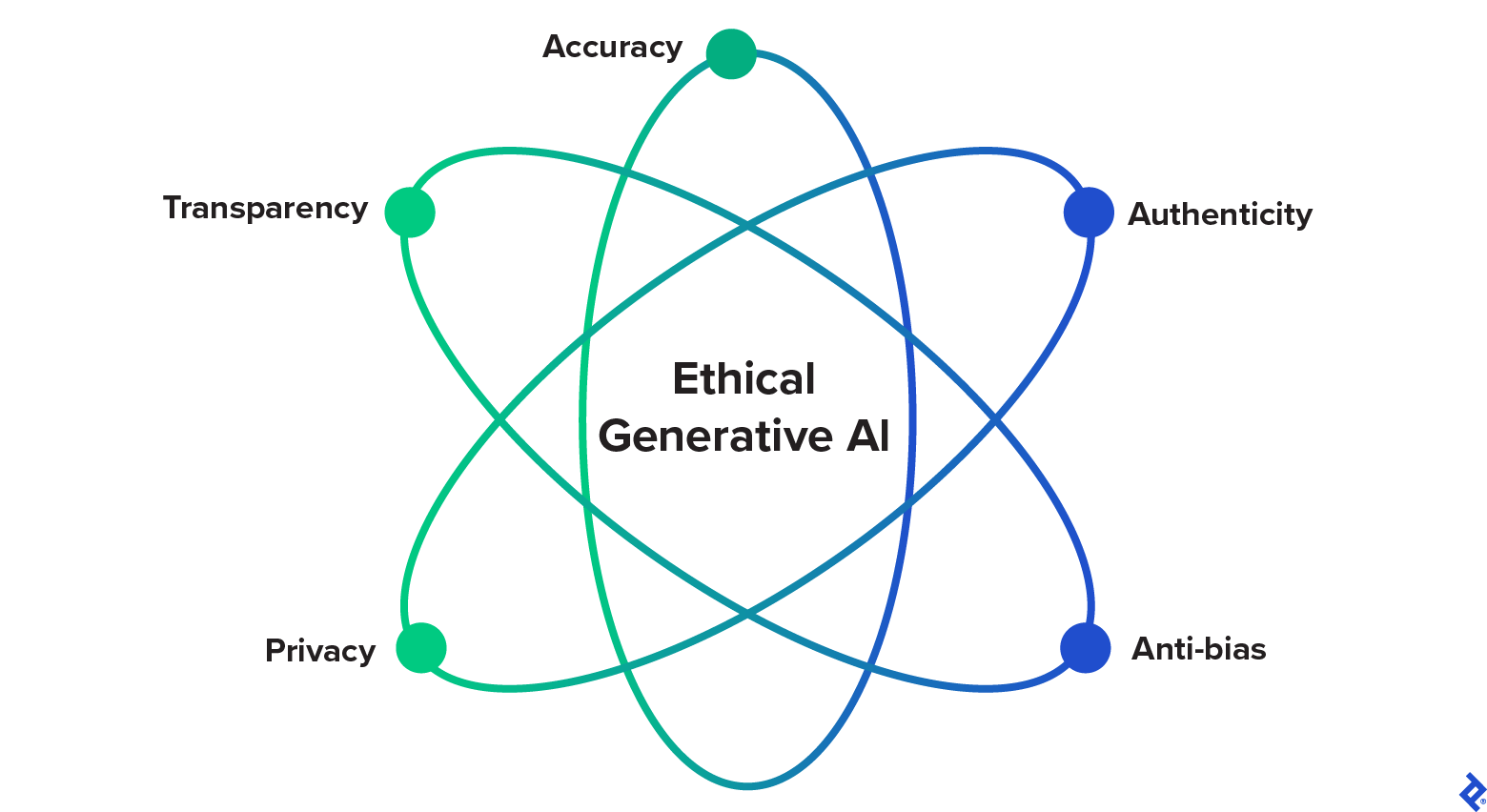
Right here, Gupta, Hotz, and Karchi suggest simply such a generative AI code of ethics for engineers, defining 5 moral pillars to implement whereas growing generative AI options. These pillars draw inspiration from different knowledgeable opinions, main accountable AI pointers, and extra generative-AI-focused steerage and are particularly geared towards engineers constructing generative AI.
1. Accuracy
With the prevailing generative AI issues round misinformation, engineers ought to prioritize accuracy and truthfulness when designing options. Strategies like verifying knowledge high quality and remedying fashions after failure will help obtain accuracy. One of the crucial distinguished strategies for that is retrieval augmented technology (RAG), a number one approach to advertise accuracy and truthfulness in LLMs, explains Hotz.
He has discovered these RAG strategies significantly efficient:
- Utilizing high-quality knowledge units vetted for accuracy and lack of bias
- Filtering out knowledge from low-credibility sources
- Implementing fact-checking APIs and classifiers to detect dangerous inaccuracies
- Retraining fashions on new knowledge that resolves information gaps or biases after errors
- Constructing in security measures akin to avoiding textual content technology when textual content accuracy is low or including a UI for person suggestions
For purposes like chatbots, builders may additionally construct methods for customers to entry sources and double-check responses independently to assist fight automation bias.
2. Authenticity
Generative AI has ushered in a brand new age of uncertainty relating to the authenticity of content material like textual content, photographs, and movies, making it more and more essential to construct options that may assist decide whether or not or not content material is human-generated and real. As talked about beforehand, these fakes can amplify misinformation and deceive people. For instance, they may affect elections, allow id theft or degrade digital safety, and trigger situations of harassment or defamation.
“Addressing these dangers requires a multifaceted strategy since they carry up authorized and moral issues—however an pressing first step is to construct technological options for deepfake detection,” says Karchi. He factors to numerous options:
- Deepfake detection algorithms: “Deepfake detection algorithms can spot delicate variations that might not be noticeable to the human eye,” Karchi says. For instance, sure algorithms might catch inconsistent habits in movies (e.g., irregular blinking or uncommon actions) or examine for the plausibility of organic indicators (e.g., vocal tract values or blood circulate indicators).
- Blockchain know-how: Blockchain’s immutability strengthens the ability of cryptographic and hashing algorithms; in different phrases, “it might probably present a method of verifying the authenticity of a digital asset and monitoring adjustments to the unique file,” says Karchi. Displaying an asset’s time of origin or verifying that it hasn’t been modified over time can assist expose deepfakes.
- Digital watermarking: Seen, metadata, or pixel-level stamps might assist label audio and visible content material created by AI, and plenty of digital textual content watermarking strategies are underneath improvement too. Nonetheless, digital watermarking isn’t a blanket repair: Malicious hackers might nonetheless use open-source options to create fakes, and there are methods to take away many watermarks.
You will need to observe that generative AI fakes are enhancing quickly—and detection strategies should catch up. “This can be a repeatedly evolving subject the place detection and technology applied sciences are sometimes caught in a cat-and-mouse sport,” says Karchi.
3. Anti-bias
Biased programs can compromise equity, accuracy, trustworthiness, and human rights—and have severe authorized ramifications. Generative AI initiatives needs to be engineered to mitigate bias from the beginning of their design, says Karchi.
He has discovered two strategies particularly useful whereas engaged on knowledge science and software program initiatives:
- Numerous knowledge assortment: “The information used to coach AI fashions needs to be consultant of the varied situations and populations that these fashions will encounter in the actual world,” Karchi says. Selling various knowledge reduces the probability of biased outcomes and improves mannequin accuracy for varied populations (for instance, sure skilled LLMs can higher reply to completely different accents and dialects).
- Bias detection and mitigation algorithms: Knowledge ought to endure bias mitigation strategies each earlier than and through coaching (e.g., adversarial debiasing has a mannequin be taught parameters that don’t infer delicate options). Later, algorithms like equity by consciousness can be utilized to guage mannequin efficiency with equity metrics and regulate the mannequin accordingly.
He additionally notes the significance of incorporating person suggestions into the product improvement cycle, which may present precious insights into perceived biases and unfair outcomes. Lastly, hiring a various technical workforce will guarantee completely different views are thought of and assist curb algorithmic and AI bias.
4. Privateness
Although there are a lot of generative AI issues about privateness relating to knowledge consent and copyrights, right here we deal with preserving person knowledge privateness since this may be achieved through the software program improvement life cycle. Generative AI makes knowledge weak in a number of methods: It could leak delicate person info used as coaching knowledge and reveal user-inputted info to third-party suppliers, which occurred when Samsung firm secrets and techniques had been uncovered.
Hotz has labored with purchasers eager to entry delicate or proprietary info from a doc chatbot and has protected user-inputted knowledge with a commonplace template that makes use of a couple of key elements:
- An open-source LLM hosted both on premises or in a non-public cloud account (i.e., a VPC)
- A doc add mechanism or retailer with the non-public info in the identical location (e.g., the identical VPC)
- A chatbot interface that implements a reminiscence element (e.g., through LangChain)
“This methodology makes it potential to attain a ChatGPT-like person expertise in a non-public method,” says Hotz. Engineers may apply comparable approaches and make use of inventive problem-solving ways to design generative AI options with privateness as a prime precedence—although generative AI coaching knowledge nonetheless poses vital privateness challenges since it’s sourced from web crawling.
5. Transparency
Transparency means making generative AI outcomes as comprehensible and explainable as potential. With out it, customers can’t fact-check and consider AI-produced content material successfully. Whereas we might not have the ability to remedy AI’s black field drawback anytime quickly, builders can take a couple of measures to spice up transparency in generative AI options.
Gupta promoted transparency in a variety of options whereas engaged on 1nb.ai, an information meta-analysis platform that helps to bridge the hole between knowledge scientists and enterprise leaders. Utilizing computerized code interpretation, 1nb.ai creates documentation and offers knowledge insights by a chat interface that staff members can question.
“For our generative AI function permitting customers to get solutions to pure language questions, we supplied them with the unique reference from which the reply was retrieved (e.g., an information science pocket book from their repository).” 1nb.ai additionally clearly specifies which options on the platform use generative AI, so customers have company and are conscious of the dangers.
Builders engaged on chatbots could make comparable efforts to disclose sources and point out when and the way AI is utilized in purposes—if they’ll persuade stakeholders to agree to those phrases.
Suggestions for Generative AI’s Future in Enterprise
Generative AI ethics will not be solely essential and pressing—they are going to seemingly even be worthwhile. The implementation of moral enterprise practices akin to ESG initiatives are linked to larger income. When it comes to AI particularly, a survey by The Economist Intelligence Unit discovered that 75% of executives oppose working with AI service suppliers whose merchandise lack accountable design.
Increasing our dialogue of generative AI ethics to a big scale centering round complete organizations, many new issues come up past the outlined 5 pillars of moral improvement. Generative AI will have an effect on society at massive, and companies ought to begin addressing potential dilemmas to remain forward of the curve. Toptal AI consultants recommend that firms may proactively mitigate dangers in a number of methods:
- Set sustainability targets and scale back power consumption: Gupta factors out that the price of coaching a single LLM like GPT-3 is big—it’s roughly equal to the yearly electrical energy consumption of greater than 1,000 US households—and the price of each day GPT queries is even larger. Companies ought to put money into initiatives to reduce these damaging impacts on the surroundings.
- Promote variety in recruiting and hiring processes: “Numerous views will result in extra considerate programs,” Hotz explains. Variety is linked to elevated innovation and profitability; by hiring for variety within the generative AI business, firms scale back the chance of biased or discriminatory algorithms.
- Create programs for LLM high quality monitoring: The efficiency of LLMs is extremely variable, and analysis has proven vital efficiency and habits adjustments in each GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 from March to June of 2023, Gupta notes. “Builders lack a secure surroundings to construct upon when creating generative AI purposes, and corporations counting on these fashions might want to repeatedly monitor LLM drift to persistently meet product benchmarks.”
- Set up public boards to speak with generative AI customers: Karchi believes that enhancing (the considerably missing) public consciousness of generative AI use circumstances, dangers, and detection is important. Firms ought to transparently and accessibly talk their knowledge practices and supply AI coaching; this empowers customers to advocate in opposition to unethical practices and helps scale back rising inequalities brought on by technological developments.
- Implement oversight processes and evaluation programs: Digital leaders akin to Meta, Google, and Microsoft have all instituted AI evaluation boards, and generative AI will make checks and balances for these programs extra essential than ever, says Hotz. They play a vital position at varied product levels, contemplating unintended penalties earlier than a undertaking’s begin, including undertaking necessities to mitigate hurt, and monitoring and remedying harms after launch.
As the necessity for accountable enterprise practices expands and the earnings of such strategies acquire visibility, new roles—and even complete enterprise departments—will undoubtedly emerge. At AWS, Hotz has recognized FMOps/LLMOps as an evolving self-discipline of rising significance, with vital overlap with generative AI ethics. FMOps (basis mannequin operations) contains bringing generative AI purposes into manufacturing and monitoring them afterward, he explains. “As a result of FMOps consists of duties like monitoring knowledge and fashions, taking corrective actions, conducting audits and threat assessments, and establishing processes for continued mannequin enchancment, there may be nice potential for generative AI ethics to be carried out on this pipeline.”
No matter the place and the way moral programs are included in every firm, it’s clear that generative AI’s future will see companies and engineers alike investing in moral practices and accountable improvement. Generative AI has the ability to form the world’s technological panorama, and clear moral requirements are very important to making sure that its advantages outweigh its dangers.
[ad_2]