
[ad_1]
Nominate now for the 3D Printing Business Awards 2023.
Scientists at Jiangnan College, China, have developed a novel method for 3D printing support-free advanced ceramic buildings.
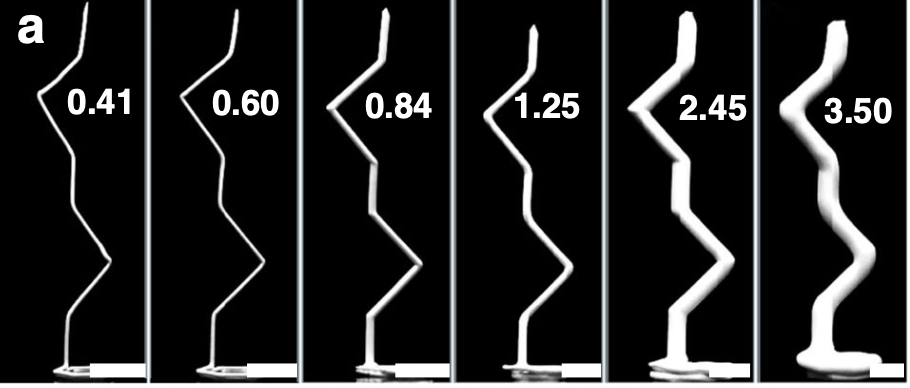
Revealed in Nature Communications, the analysis highlights the brand new technique’s in-situ curing capabilities for multi-scale filaments with diameters starting from 0.41 mm to three.50 mm.
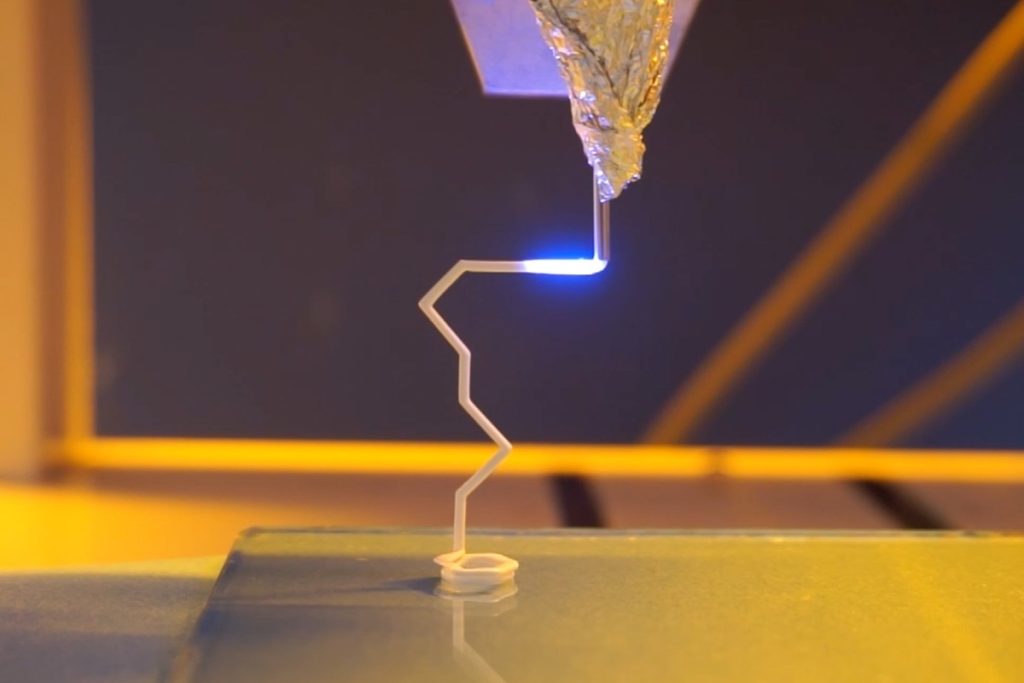
This ceramic 3D printing technique leverages a mixture of direct ink writing (DIW) and near-infrared (NIR) light-induced up-conversion particle-assisted photopolymerization. As a part of a two-step course of, stress is first utilized to extrude the ceramic slurry. A 980 nm NIR laser is then focused on the slurry because it exits the nozzle, instantly solidifying and curing the fabric in situ via photopolymerization. This permits for the 3D printing of ceramic buildings that may be “freely stretched in house with out assist,” in response to the researchers.
This new method holds potential for a lot of key verticals, together with equipment, electronics, power, aerospace, and biomedicine. Certainly, the purposeful ceramics used on this analysis possess a spread of fantastic mechanical properties reminiscent of structural stability, corrosion resistance, and excessive temperature resistance.
“This technique will convey extra innovation to the unsupported 3D manufacturing of advanced form ceramics,” the researchers declare, including that “The unsupported additive manufacturing expertise primarily based on NIR-DIW opens up greater levels of freedom for ceramic additive manufacturing design.”
The authors added that “the NIR-DIW methodology will get additional expanded, and ceramic geometries produced with out assist will assist generate extra improvements and widespread the appliance of additive manufacturing applied sciences.”
The demand for support-free 3D printing
Conventional 3D printing processes, reminiscent of digital mild processing, stereolithography, and binder jetting, can produce excessive decision ceramic components at good charges of manufacturing. Nevertheless, sure geometries, for instance large-span (buildings that span a big distance with out intermediate helps) and particular formed components, require extra assist buildings throughout 3D printing – in response to the researchers.
The removing of those helps can pose challenges, reminiscent of lengthy processing occasions, greater value, dimensional imprecision and poor floor high quality. Moreover, micro-cracking can usually happen throughout assist removing, while inner assist removing isn’t at all times viable for specifically designed buildings with poor openness and sophisticated shapes.
By means of this new in-situ NIR-DIW course of, ceramic buildings with versatile geometries and traits could be 3D printed with out assist buildings. Moreover, it’s claimed that this technique reduces post-processing workloads and 3D printing time, permits better throughput, improves manufacturing precision, and lowers materials utilization.
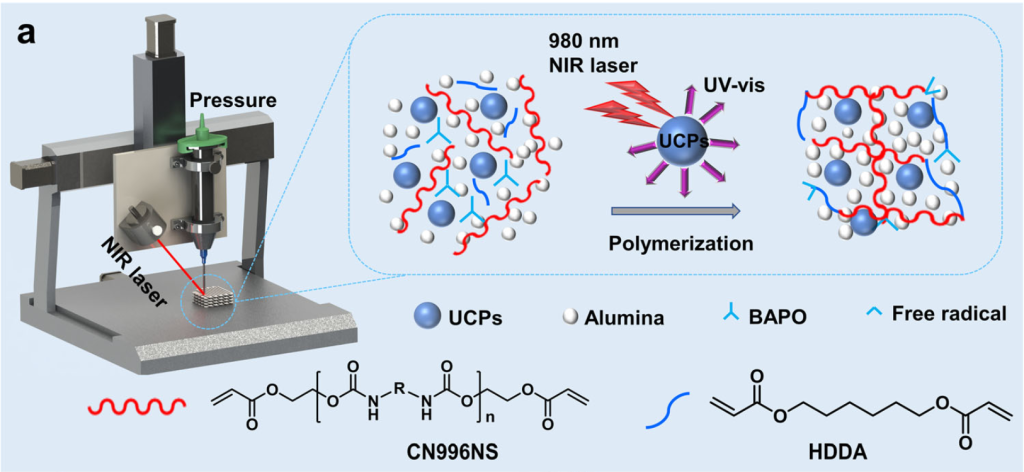
The NIR-DIW 3D printing course of
On this new technique, up-conversion particles (UCPs)-assisted photopolymerization (UCAP) induced by NIR mild was coupled with DIW to permit for on-demand curing at managed charges.
Throughout this course of, a 980 nm NIR laser is focused on the ceramic slurry throughout extrusion. By adjusting the irradiation depth and extrusion velocity, the slurry could be near-instantaneously solidified and cured in situ. Moreover, the 3D printing course of doesn’t require heating or cooling, making it “steady and clean.”
Utilizing this system, the researchers succeeded in near-instantaneously solidifying multi-scale filaments with diameters starting from 0.41 mm to three.5mm, at speeds of as much as 41 mm/s. Through the mission, the scientists 3D printed a spread of support-free ceramic buildings, together with torsion springs and cantilevers.
The analysis staff additionally demonstrated that NIR mild gives drastically improved curing depths over UV mild. As an illustration, when testing the remedy depth of the ceramic slurry, the researchers discovered that UV mild reached a curing depth of 1.02 mm in round two minutes. Nevertheless, with NIR mild, the curing depth reached as much as 3.81 mm in simply 3 seconds of publicity.
Assist-free 3D printing
This isn’t the primary time researchers have sought to develop support-free 3D printing capabilities. Final yr, scientists from Colorado State College introduced that that they had developed a brand new technique of 3D printing carbon fiber-reinforced composite components with out the necessity for assist buildings.
This system centered round a specially-developed thermoset resin and a novel curing course of known as frontal polymerization. By means of this course of, the 3D printed materials cures as it’s being extruded, which means that the half turns into inflexible virtually instantly with none exterior UV or IR radiation. This course of permits support-free 3D printing.
Again in 2021, 3D printing software program developer Dyndrite launched a set of software program APIs enabling 3D printer producers to extra simply implement superior options reminiscent of support-free metallic 3D printing. The API works by segmenting the half at resolutions finer than the minimal characteristic measurement. This permits for distinctive support-free processing parameters to be assigned to totally different volumes inside an element.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Business publication to maintain updated with the most recent 3D printing information. You can even comply with us on Twitter, like our Fb web page, and subscribe to the 3D Printing Business Youtube channel to entry extra unique content material.
Are you curious about working within the additive manufacturing business? Go to 3D Printing Jobs to view a choice of out there roles and kickstart your profession.
The support-free ceramic 3D printing course of in motion. Picture by way of Jiangnan College.
[ad_2]